The Importance of Endpoint Data Protection
Digital transformation has elevated the significance of data in modern enterprises, touching every aspect from production to sales. In this context, data is informative and integral to a company's productivity. Endpoint devices, such as computers and mobile phones, serve as the generators and processors of this critical data. Because these devices interact with external networks, they are particularly susceptible to security risks, making endpoint protection vital for the ongoing success of the business.
The rise of practices like Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), remote work, and mobile office environments has complicated endpoint security. These changes have expanded the attack surface for threats such as ransomware, zero-day vulnerabilities, and data breaches. As a result, ensuring the security of endpoint devices has become an increasingly pressing challenge.
In this article, we will delve into the complexities of endpoint data protection, offering a comprehensive solution for data protection on these devices.
Top Endpoint Data Security Risks
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts data on a device or network. The attackers then demand payment for the decryption key. The risk is high because data is rendered inaccessible, and there is no guarantee that paying the ransom will lead to the data's restoration. The latest statistics from IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 indicate that the average cost for ransomware breaches was $5.13 million, a 13% increase from the previous year's average of $4.54 million.
- Data Breaches: A data breach occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to confidential information. This is usually achieved through exploiting system vulnerabilities or using social engineering tactics like phishing attacks. Sensitive data like customer information, financial records, or intellectual property could be stolen or exposed. The risks include financial loss, reputational damage, and compliance violations. The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 states that the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million, a rise of about 15% over three years.
- Remote Work: Remote work introduces risks by expanding the boundary of the corporate network to include home networks and public Wi-Fi networks, which are generally less secure. Additionally, the devices might be shared among family members, increasing the likelihood of accidental data exposure or malware infection. In a 2023 survey, Statista found that 72% of global respondents were either very concerned or somewhat concerned about the online security risks posed by employees working remotely.
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): BYOD policies allow employees to use their personal devices for work purposes. While this offers flexibility and cost savings, it also brings risks associated with a lack of control over these external devices. They may not be as securely configured or regularly updated as company-owned endpoints, thus serving as weak links in the security chain. According to the 2021 BYOD Security Report by Cybersecurity Insiders, data leakage/loss was the number one security concern related to BYOD at 62%.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats come from people within the organization, like employees or contractors. Malicious insiders intentionally steal or sabotage data, whereas accidental insiders might unwittingly expose data through mistakes like sending information to the wrong person. Both scenarios are risky because they bypass traditional security measures, which usually focus on external threats. The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report mentions that internal actors are responsible for 1 in 5 of the analyzed incidents. However, despite constituting around 20% of the breaches, these internal threats resulted in the loss of over 1 billion records, compared to the 200 million records lost to external threats.
- Hardware and Software Failure: Hardware and software failures can lead to data loss or temporary unavailability. For example, a hard drive failure can result in the loss of important files, while software bugs can compromise the functionality of security features. Such failures disrupt operations and can lead to data being inaccessible, posing a significant business risk.
Traditional Endpoint Data Protection Solutions
Organizations typically deploy various products and solutions to protect endpoint data. These include:
- Anti-Virus: Detects and removes malware and viruses that could compromise data.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): Distributes data across multiple disks, which provides redundancy and prevents data loss in case of a disk failure.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Software: Monitors and controls data transfer, ensuring sensitive data remains within a secure network and preventing unauthorized access or data leakage.
- Data Encryption Software: Converts data into a coded form, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users.
- Data Backup Software: Creates copies of data that can be restored in the event of data loss or corruption.
Challenges of Traditional Endpoint Data Protection Solutions
- Security Gaps: Relying on a limited number of solutions can lead to gaps in security coverage. For example, while anti-virus software can effectively protect against known malware, it struggles against new variants, zero-day attacks, and insider threats. Similarly, While RAID can protect against data loss due to disk failures, it doesn't protect against data loss that can occur due to system-level failures or software corruption. Moreover, it only covers the data in a singular host system, making it a vulnerability if that host system is compromised.
- Difficulty Adapting to New Work Models: Traditional endpoint data protection solutions struggle to adapt to the changing landscape of remote work and mobile offices. Issues such as user identification, secure data access, and safe data sharing across diverse devices have become increasingly problematic for businesses. For example, DLP solutions are designed to monitor and control data transfers within networks. With the increase in remote work, data is being accessed and transferred across various networks, making the traditional DLP systems less effective or more complex to manage.
- Performance Degradation: The use of multiple software solutions for endpoint data protection can lead to system performance degradation. This affects not only the system resources but also user productivity, as resources are diverted to run non-business-critical software.
- Management Complexity: Each solution typically comes with its own independent management platform, making system administration more complex and increasing operational costs.
Endpoint Data Protection Using VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that allows you to run a virtual desktop inside virtual machines (VMs) hosted on servers in a data center. Users can access their virtual desktops remotely through an endpoint device, like a laptop or thin client, providing the experience of using a local desktop.
VDI provides a more secure environment by design as data is stored in backend servers instead of locally on endpoints. This makes it more difficult for hackers to access the data even when endpoints are compromised.
Sangfor VDI is a one-stop solution that integrates desktop, server, and application virtualization using Sangfor HCI (Hyperconverged Infrastructure). It offers a comprehensive range of security mechanisms that provide end-to-end endpoint data protection, covering users and clients to the underlying infrastructure. It helps organizations prevent sensitive data loss and breaches and meet compliance standards.
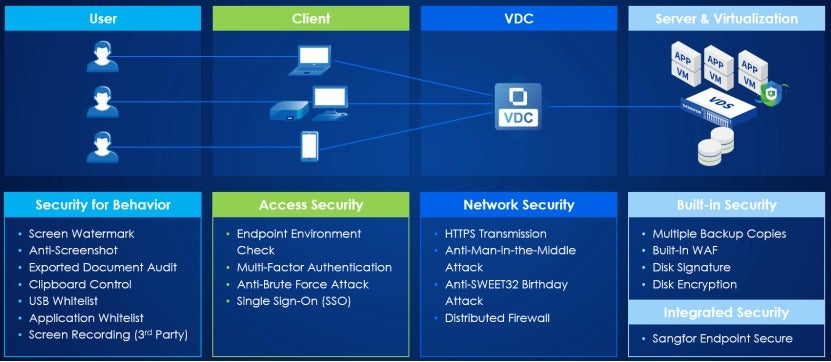
Integrated Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Sangfor is the industry's first vendor to integrate EDR capabilities (Sangfor Endpoint Secure) into a VDI solution. When Sangfor Endpoint Secure detects a threat in a virtual machine (VM), Sangfor HCI automatically creates snapshots of the affected VM and related VMs to minimize data loss.
- Endpoint Secure detects a threat
- Endpoint Secure updates Endpoint Secure Manager
- Endpoint Secure Manager updates Sangfor HCI
- Sangfor HCI creates a snapshot of VMs

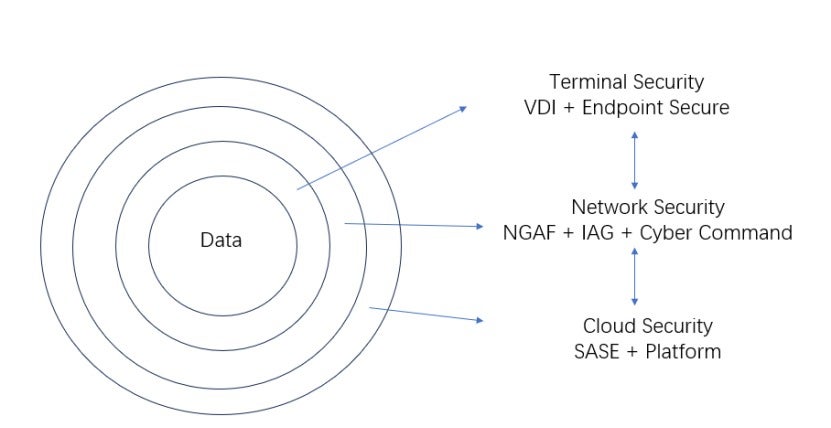
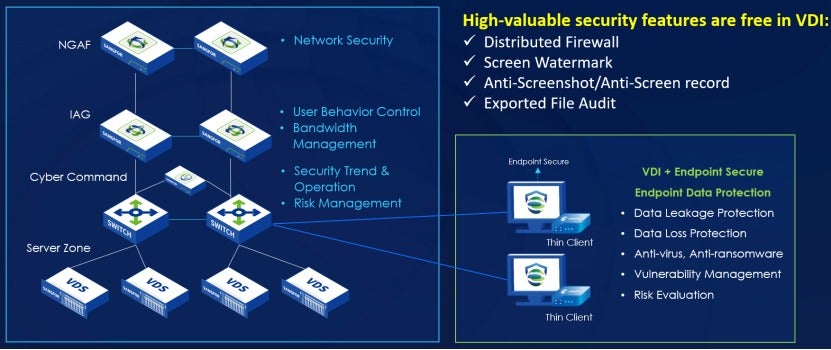
Defense in Depth
Sangfor VDI adopts a defense-in-depth (DiD) strategy that protects data across endpoint, network, and cloud.
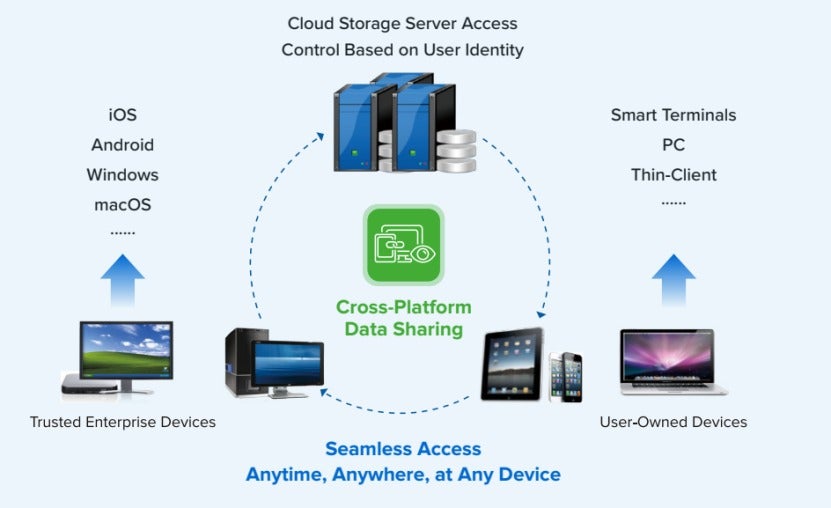
Seamless Access
Consistent data enables seamless work anytime, anywhere, and on any devices.