As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, the traditional office environment has undergone a remarkable transformation. The increasing need for seamless collaboration, enhanced productivity, and remote accessibility has given rise to a modern solution that adapts to these evolving demands – the Digital Workspace.
What is a Digital Workspace?
A digital workspace is an integrated platform comprising all the tools, applications, data, and collaboration capabilities required for individuals and teams to work effectively and efficiently. It is designed to provide a seamless user experience, enabling employees to access their work-related resources and tools from anywhere and on any device with an internet or local network connection.

Examples of Digital Workspace Technologies and Solutions
Digital workspaces include cloud-based productivity suites like Microsoft 365 and collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams. Here is a list of the main types of digital workspace technologies with examples of solutions for each technology.
| Digital Workspace Technology | Example Digital Workspace Solutions |
|---|---|
| Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) | VMware Horizon, Citrix XenDesktop and XenApp, Sangfor aDesk |
| Productivity Suites | Microsoft 365, Google Workspace |
| Communication and Collaboration Tools | Microsoft Teams, Slack |
| Video Conferencing Tools | Zoom, Cisco Webex |
| Enterprise Social Networks (ESN) | Yammer, Workplace by Facebook |
| Cloud Storage and File Sharing | Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive |
| Knowledge Management Systems | Microsoft SharePoint, Confluence |
| Project Management Software | Asana, Trello, Jira |
| Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) | Microsoft Intune, VMware Workspace ONE |
Explore VDI as Your Digital Workspace Solution
In this article, we will focus on a specific type of digital workspace – Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI). We will explain what VDI is, how it works, its advantages over traditional PCs, and the various use cases it is best suited to. We aim to provide you with a fundamental understanding of VDI and invite you to delve deeper into the technology to decide if it’s the right digital workspace solution for your organization.
What is VDI?
VDI is a technology that enables users to access virtualized computer desktops hosted on remote servers via the internet or a local network. VDI offers benefits such as greater flexibility, scalability, security, and centralized management of desktop computing resources compared to traditional PCs.
How Does VDI Work?
Unlike traditional PCs, where the operating system, applications, and data reside locally on the device, VDI centralizes everything on servers in a data center. Virtual desktops are created and run on virtual machines (VMs) hosted on the server. Each VM houses a separate virtual desktop, and a single server can host numerous VMs.
When a user wants to access their virtual desktop, they connect to it through a software program known as a connection broker. This broker establishes a link to the server, which then streams a real-time image of the user's virtual desktop to their device as if using a local desktop. This setup allows users to access their virtual desktops from any device or location with a network connection.
How is VDI deployed?
The main deployment models of VDI are:
· As software installed on on-premises servers (legacy or private cloud)
· As a public cloud service, known as Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS)
The Benefits of a Digital Workspace with VDI
VDI offers numerous advantages over a PC-based workspace. In the following section, we will discuss the benefits of VDI by contrasting them with the challenges posed by traditional PCs.
1. Accessibility
PC: In a traditional PC setup, employees are generally tied to a specific physical device. It’s difficult for them to access their desktops from different locations without having to carry the device from place to place.
VDI: Because virtual desktops run in VMs hosted in a data center, employees can easily access their desktops and applications from any location and on any device, as long as they have an internet or network connection. This allows employees to work remotely in a consistent work environment, which improves the employee experience and productivity.
2. Security
PC: Data is stored locally on individual PCs, increasing the risk of data breaches due to device theft, loss, or unauthorized access. Local endpoints are also susceptible to malware and cyber-attacks.
VDI: With VDI, the user's virtual desktop and data are kept separate from the local PC desktop. This isolation means that even if the local PC is compromised by malware or a cyber-attack, the data stored on backend servers with multiple copies remains protected and unaffected. Moreover, VDI solutions typically provide data protection mechanisms. For example, admins can set policies that prohibit users from copying data from their virtual desktop onto the local desktop or USB drives. Security controls like this ensure that employees don’t leak sensitive business information like intellectual property, either accidentally or maliciously.
3. Scalability
PC: Scaling traditional PC environments can be complex and costly, requiring significant hardware investment and resource planning.
VDI: VDI is highly scalable and adaptable to changing business requirements. IT admins can create additional VMs or adjust their resources to accommodate more users or higher performance needs. VDI deployments can be quickly scaled out by provisioning more servers and scaled up in performance with more CPUs, memory, and storage. The cloud-based infrastructure also supports elastic computing, which dynamically adjusts resources based on demand without prior planning. This is especially beneficial for organizations with seasonal or fluctuating workloads throughout the year.
4. Operations and Maintenance
PC: Managing individual PCs can be labor-intensive and prone to inconsistencies in software configurations and updates.
VDI: Virtual desktops are significantly easier to manage compared to traditional PCs. With VDI, IT admins can centrally manage and deploy virtual desktops to employees, reducing the need for individual machine configurations and maintenance. IT teams can centrally manage user access, security policies, software updates, and patches, ensuring consistent and streamlined desktop management. Additionally, troubleshooting and support become more efficient as admins can remotely access and troubleshoot virtual desktops, reducing the need for on-site visits.
5. Costs
PC: Traditional PC setups require more physical endpoints, leading to higher hardware and maintenance costs. Hardware resources are often underutilized, leading to wastage.
VDI: While the initial costs of VDI will be 10-30% higher than traditional PCs, implementing VDI can result in significant cost savings in the longer term. With fewer physical endpoints, companies reduce hardware investment and save on energy costs. Thin clients consume less power and have a longer lifespan than traditional desktops, further reducing costs. Additionally, centralized management leads to lower hardware maintenance expenses and better resource utilization, optimizing overall IT expenditures.
| Cost Item | VDI | Traditional PC |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Costs | Server + Thin Client + EDR | PC + EDR |
| IT Labor Costs | One IT staff per 500-1000 users | One IT staff per 100 users |
| Electricity Consumption | Server: 600-1000W Thin Client: 20W |
PC: 350W |
| Hardware Depreciation | Servers in a standard DC have a long lifecycle. Easy to replace thin clients in the office. Hardware lifecycle = 5-6 Years |
High damage rate (Damaged by user, continuous operation, non-standard environment) Hardware lifecycle = 3-4 Years |
| Increased User Productivity | Remote/mobile work increases by 20-50% | / |
| Business Interruption Costs | 1-2 hours per user per year | 4-8 hours per user per year |
| Data Breach Costs | / | Global average cost of a data breach: $4.45M USD |
The Use Cases of VDI
The numerous benefits of VDI make it a highly versatile digital workspace solution, providing a range of practical applications in various scenarios. Let's now explore six compelling use cases where VDI is a game-changer.
- Secure Office: VDI brings a secure office environment by centralizing data and applications in the data center, protecting against malware, cyber-attacks, and insider threats. Security mechanisms like encrypted connections, behavior control, and access control further enhance protection. This makes VDI an ideal solution for industries that handle highly sensitive data and need to comply with strict data security and privacy regulations, such as BFSI, healthcare, and government.
- Remote Work: VDI offers remote workers the ability to securely access their virtual desktops and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This fosters employee productivity while maintaining data security and a consistent user experience.
- Training Rooms: VDI reduces setup time and simplifies maintenance in training rooms. Trainers can swiftly deploy virtual desktops using standard templates and restore desktops to a clean state after each session for consistent learning experiences.
- Call Centers: VDI provides elasticity, allowing call centers to adjust the number of desktops based on call volume fluctuations. Multiple agents can share the same seat, and the VMs are restored after each use. This enhances hardware utilization rates and reduces hardware costs.
- 3D Work: VDI provides remote access to powerful graphical processing capabilities, enabling users to perform resource-intensive 3D modeling and rendering tasks without requiring high-end local hardware, resulting in workstation cost savings. Centralized software management and optimized license usage further reduce professional software license costs.
- Production Lines: VDI enhances business continuity on production lines as critical apps run on virtual desktops in the data center. In the event of a hardware failure, employees can quickly resume their work from alternative devices without disrupting operations.
Sangfor aDesk VDI
Sangfor aDesk is a revolutionary VDI solution engineered to help organizations transition seamlessly from a traditional PC-based workspace to a modern digital workspace platform.
Sangfor aDesk is a One-Stop Secure VDI solution that integrates the critical components, including the thin client, hypervisor, server, virtual desktop controller (VDC), and security features in a single offering. It is delivered with Sangfor HCI, for which Sangfor ranks as one of the world's leading vendors based on Gartner Market Share data.
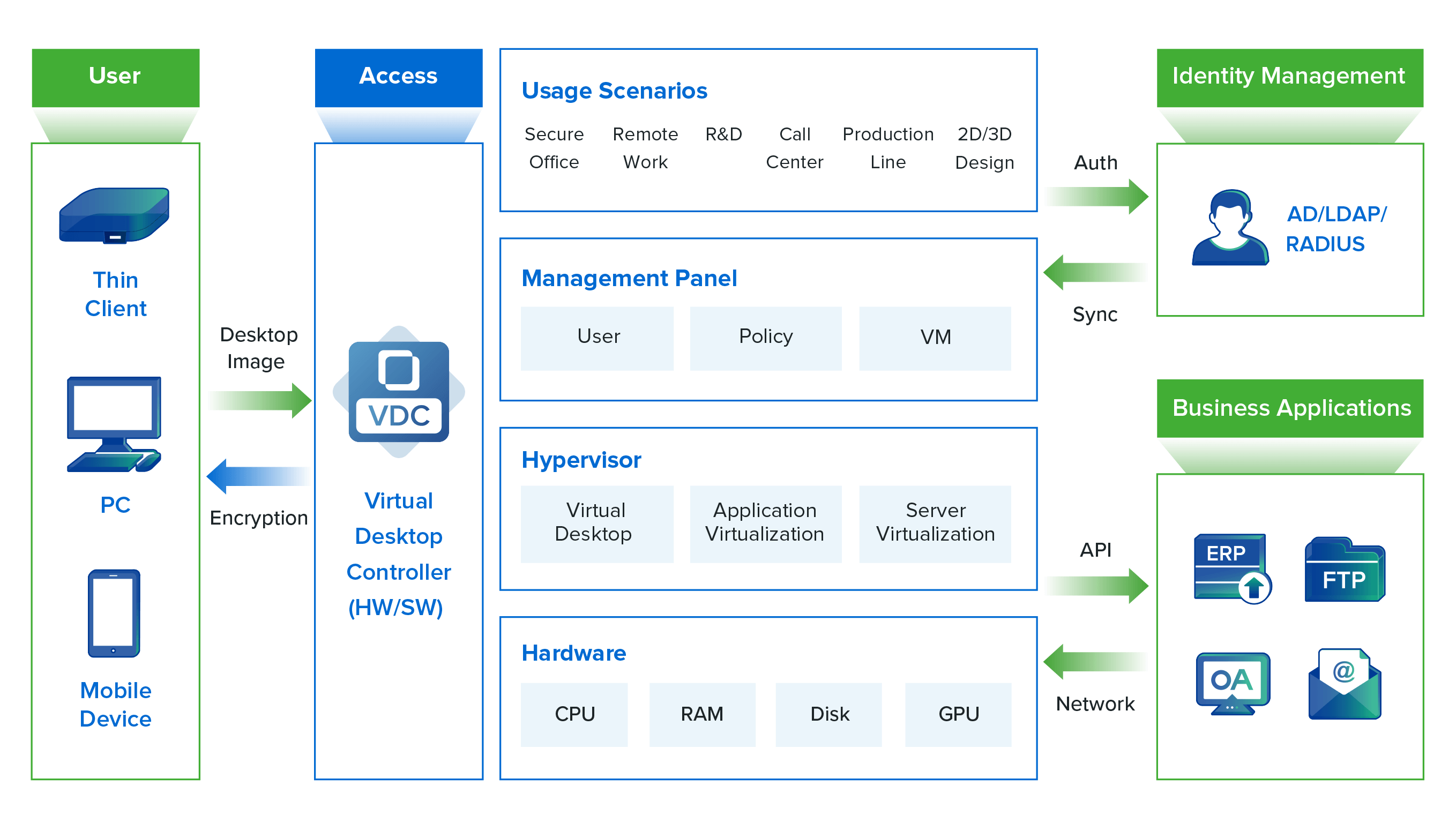
Sangfor aDesk VDI Architecture
As a leading cybersecurity and cloud computing vendor, Sangfor seamlessly integrates its security expertise into its cloud and infrastructure products. Sangfor aDesk is packed with a host of vital security features that protect against sensitive data leakage and cyber threats. These include anti-screenshot, screen watermark, USB and clipboard control, file export audit, built-in web application firewall (WAF), and distributed firewall. These features are provided without additional license costs, offering a cost-effective secure VDI solution. Customers who wish to strengthen endpoint protection can further make use of our VDI + EDR solution. Organizations can rest assured and trust that their data remains protected with Sangfor VDI.
Sangfor aDesk has an impressive track record of over 2.2 million virtual desktop deployments. Notable customers include Foxconn, Teleperformance, EFU Life, JS Bank, Global Care Hospital, CJ Logistics, and Lotte E&C. Recently published Gartner Market Share data ranked Sangfor as the 3rd largest vendor of VDI in the Asia-Pacific.
Visit the Sangfor aDesk VDI webpage to discover its full range of features and benefits, explore success stories and customer testimonials, and more!





