Nefilim Ransomware Invades SPIE Group
Introduction
Nefilim ransomware first appeared in March 2020 as a newly developed ransomware designed to spread through various methods including spam, P2P file sharing, free software installation, malicious websites, torrent websites, and vulnerable RDP platforms.
Research analysis discovered that a considerable part of the code is shared with NEMTY, another popular ransomware family, however the exact relationship between NEMTY and Nefilim/Nephilim is currently unclear.
Development
Recently, Nefilim ransomware was detected when it invaded SPIE Group, an independent leader in European multi-technology services. SPIE Group provides multiple technical services in the energy and communications fields, with more than 47,200 employees, consolidated revenues of 6.9 billion Euro in 2019, and consolidated EBITA of 416 million Euro. After analysis, Nefilim ransomware released a total of 65,042 files contained in 18,551 data folders.

Result
Nefilim ransomware remains very active, with the number of ransomware attacks continuing to increase. Hackers not only stole victim data, but threatened them with release of the stolen information if the ransom wasn’t paid in a timely manner.
Lafayette city in Colorado, USA was forced to pay $45,000 to Nefilim operators after they were unable to restore critical files from their encrypted backup.
Introduction
On July 27, 2020 a system in Lafayette, Colorado, USA was infected by Nefilim ransomware, with malicious code affecting telephone services, e-mail and online payment reservation systems. Lafayette City did not immediately disclose the cause of their system failure, but instead invited citizens to use 911 or other numbers for emergency services.
Development
The city of Lafayette now admits that they were the victim of a ransomware attack, which encrypted their system. After a thorough inspection of the situation and cost, they considered the possibility of long-term service interruption for residents an unacceptable disadvantage. It was determined that obtaining the decryption tool was far less than the cost and time of rebuilding the data and the system, finally resulting in the city of Lafayette deciding to pay the ransom of 45,000 USD for the decryption tool to recover files.
Result
The small ransom demand by the attackers indicates that this was not one of the more powerful ransomware variant. For example, Maze, REvil or Clop ransomware usually demand much higher ransoms.
Dharma Ransomware Operator Creates a Hacking Toolkit
Introduction
Dharma ransomware is one of the longest-running ransomware series today. First discovered in March 2016, it was called CrySiS, but its master decryption key was leaked in a post on the Bleeping Computer forum in November 2016. Soon after, a new variant of the ransomware was released, appending the .dharma extension to the encrypted files. These variants are most likely due to subsequent users purchasing the source code and then modifying and distributing it. Since then, this family and its constantly emerging new variants have been called Dharma. Unlike other RaaS operations that target large companies with ransoms reaching $100,000 million, Dharma's ransom is generally lower, with an average demand of about $9,000.

Development
Recently, the operator has provided a new toolkit based on RaaS. Unlike many private ransomware RaaS operators that only cooperate with experienced hackers, the Dharma operator provides this ready-made toolkit, which allows anyone to perform Illegal activities which can easily invade the network, with its lower price reflecting their desire to lower the entry barrier for members.
Results
By providing toolkits and usage documentation, Dharma recruits more potential users and buyers. Lowering the cost threshold increases the number of user groups, enabling a much large user group to establish a wide attack network to catch as many victims as possible. The victim is initially asked for a smaller ransom, which may increase to a larger amount with more far reaching impacts if the ransom isn’t paid.
Sangfor Ransomware Solution
Sangfor's Security Solution for Ransomware provides a holistic solution to stop ransomware attacks in real-time. The solution is robust enough to block every step in the ransomware Kill Chain, but modular enough to be tailored to any organization.
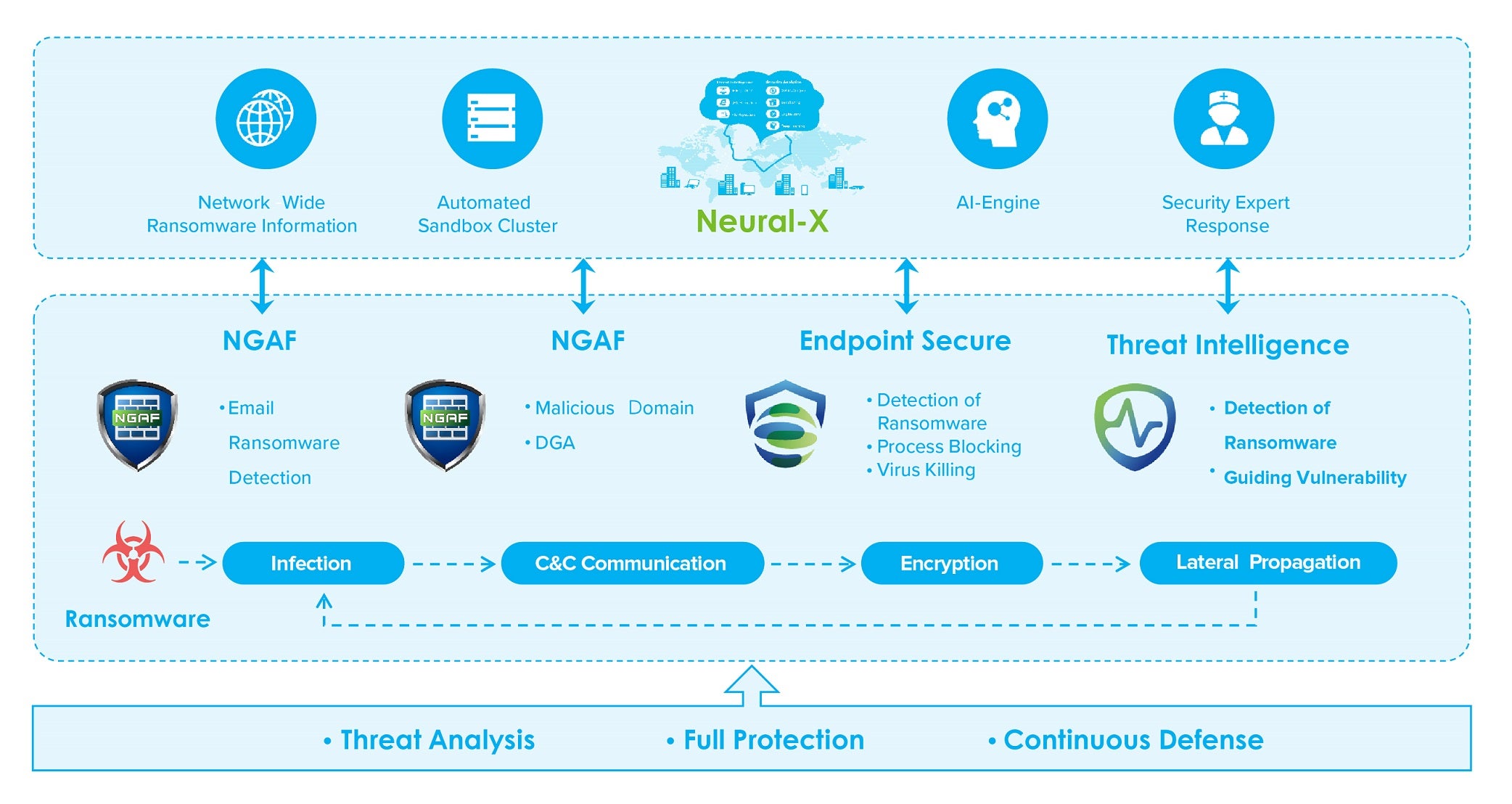
Cloud (Neural-X)
• Cloud Monitoring Service: Detects existing exploits or vulnerabilities including RDP port exposure, deserialization vulnerabilities and Eternal Blue Vulnerabilities.
• Cloud Threat Intelligence: Pushing the latest ransomware intelligence.
Next Generation Firewall
• Deploy border security devices to block WEB exploits and RDP brute force attacks.
• Configure protection device to connect with the cloud defenses and directly block outbound C&C host behavior and malicious file download, based on their IP/file reputation.
Sangfor Endpoint Secure
• Endpoint Secure provides early detection of vulnerable points that are easily exploited by ransomware.
• Scan the terminal directory regularly to check for ransomware and get real-time, AI-powered analysis of ransomware behavior and get immediate isolation of infected hosts to avoid widespread infection.
Sangfor Cyber Command
• Link network and terminal data to jointly analyze suspicious behavior, monitor in real-time and provide early warning of any threats.
Ransomware Protection Video
Watch a video of a simulated ransomware attack triggered by a phishing email and see how the Sangfor Cloud-Firewall-Endpoint integrated solution can protect your organization against each step of the ransomware kill chain!
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFORMATION





