What is Network Virtualization?
Network virtualization is a transformative technology that decouples networking functions from the underlying hardware, similar to how virtual machines (VMs) abstract from physical servers.
By creating a simulated version of traditional network resources, it allows the pooling and sharing of hardware resources across a network. This approach enables the creation of multiple, independent virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, each capable of supporting its own unique set of applications and services.
The evolution from traditional networking to network virtualization marks a significant leap towards more flexible, software-driven operations. This foundational shift caters to the growing demand for efficient IT resource management which sets the stage for innovations in how businesses deploy, manage, and secure their network infrastructures.

Virtual vs. Physical Networks
The difference between virtual and physical networks is stark, with each having distinct attributes. Here is the comparison presented in a tabular form, providing a clear & concise distinction of the key points related to virtual and physical networks.
| Aspect | Virtual Networks | Physical Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Easily scaled up or down without new hardware. | Challenging to scale, often requiring new hardware. |
| Flexibility | Rapid and efficient modifications to meet application and user needs. | Less flexible; changes often require physical adjustments. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Less expensive to set up and maintain, avoiding physical hardware purchases. | More expensive due to the need for physical hardware. |
| Improved security | Isolated networks with specific security policies and configurations. | Physical security can be ensured to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Performance | Potential limitations in latency and bandwidth compared to physical networks. | Offers superior performance and lower latency. |
| Dependence on infrastructure | Relies on underlying physical infrastructure; issues can impact the virtual network. | Independent of underlying infrastructure, enhancing reliability. |
| Complexity | Requires expertise in both virtualization and networking, making management more complex. | Generally simpler to manage without the need for virtualization expertise. |
| Maintenance | Easier to manage with software updates. | Requires regular maintenance and upgrades, which can be time-consuming and costly. |
How Does Network Virtualization Work?
Network virtualization operates through a combination of sophisticated technologies and protocols that orchestrate the virtualization process. The backbone of this system includes hypervisors and Virtual Network Functions (VNFs), which play critical roles. Hypervisors enable the creation of VMs (Virtual Machines) on a single physical server, dramatically increasing efficiency. VNFs provide network services traditionally handled by physical hardware, thus enhancing flexibility and scalability.
At its core, network virtualization utilizes protocols such as VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) and NVGRE (Network Virtualization using Generic Routing Encapsulation). These protocols create a virtual overlay atop the physical network, allowing for the segregation and management of data traffic in a virtual environment.
Understanding Network Virtualization
- Network functions and resources are allocated to a virtual layer managed by a hypervisor, which acts as a virtual network adapter.
- The hypervisor oversees all nodes and links within the virtual networks, assigning resources to workloads as necessary.
- Each virtual network operates independently with the ability to have distinct policies from other networks.
- Network and security configurations attached to applications are mobile; moving an application to another server transfers all its configurations.
- New workloads created to scale an application automatically inherit pre-configured network and security policies, enhancing consistency and efficiency.
- VMs (virtual machines) and other workloads can communicate across different virtual networks through virtual switches & routers without using the physical network.
Why Network Virtualization is Important?
Network virtualization is transforming the landscape of IT infrastructure by providing unprecedented scalability, flexibility, security, and management capabilities. Here’s why this technology is crucial for modern businesses:
- Business & technological impact: Network virtualization facilitates rapid digital transformation, allowing businesses to adapt to market changes more swiftly and efficiently. By abstracting the network layer, companies can innovate without the traditional constraints imposed by physical hardware, speeding up the deployment of new applications and services. This agility supports business growth and competitive advantage in a technology-driven marketplace.
- Scalability & flexibility in IT infrastructure: One of the key benefits of network virtualization is its ability to scale resources on demand without the need for physical modifications to the network. This means businesses can easily expand their network capabilities as they grow, without significant upfront investments. Additionally, the flexibility offered by virtual networks allows for easy configuration and reconfiguration of network settings to meet evolving business needs without disrupting existing services.
- Enhanced security & management: Network virtualization improves security by isolating networks, which prevents the spread of threats across different segments. Each virtual network can be managed and monitored independently, which enhances security protocols and simplifies management tasks. Furthermore, the centralized nature of network virtualization management tools provides clear visibility and control over the entire network. This helps prevent unauthorized access and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Benefits of Network Virtualization
Network virtualization offers a multitude of benefits that significantly enhance the efficiency and security of IT infrastructures.
Cost reduction and resource optimization
By decoupling network functions from physical hardware, network virtualization reduces the need for expensive hardware investments.
Organizations can optimize their existing resources by consolidating multiple network functions onto fewer physical devices, which lowers both capital expenditures (CapEx) and operating expenses (OpEx). Moreover, the ability to dynamically allocate and reallocate resources based on demand helps avoid underutilization and overprovisioning, leading to more efficient energy use and reduced power costs.
Improved performance and reliability
Virtual networks can be configured and optimized to meet the specific needs of different applications, ensuring optimal performance.
Load balancing features distribute traffic evenly across network resources, preventing any single device from becoming a bottleneck. This enhances overall performance and improves network reliability and uptime, as issues can be isolated and resolved without affecting the entire network.
Simplified network management and automation
Network virtualization simplifies the management of network resources by abstracting the complexity of underlying physical networks.
Through centralized management interfaces, IT administrators can deploy, monitor, and manage network services with ease. Automation tools allow for the rapid provisioning of network resources. Policy-driven controls ensure that these resources are consistently applied across the network, reducing the potential for human error and streamlining operations.
Enhanced security features
The isolation provided by network virtualization is a critical security feature. Each virtual network operates independently, which limits the spread of security threats across network segments.
Additionally, virtual networks enable more precise security monitoring and faster response times to potential threats. Integrated security functions, such as virtual firewalls and intrusion detection systems, can be deployed directly within the network, enhancing security without the need for additional hardware.
Types of Network Virtualization
There are two primary types of network virtualization:
- External Network Virtualization - External virtualization connects multiple systems within a LAN to form one or more VLANs, or combines several LANs into a single VLAN, facilitating broader network management. This type virtualizes physical networks within the same LAN, potentially spanning multiple servers. It uses virtual switches and adapters to merge several physical LANs into a single virtual LAN (VLAN), streamlining the management of multiple systems collectively.
- Internal Network Virtualization - Internal virtualization focuses on a single server, using containers to isolate applications or run different operating systems. Limited to a single server, this type simulates a physical network using software containers and specific code, enhancing performance and ensuring consistent application functionality. VMs on this server can communicate internally without external networks.
Network Virtualization Examples
Some common examples of network virtualization are the following:
- Overlay Networks: These are virtual networks built over the existing physical network, using encapsulation protocols like VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN). Overlay networks enable the coexistence of multiple virtual networks on the same physical infrastructure, ideal for multi-tenant environments like cloud services.
- Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs): VLANs help segment a physical network into multiple logical networks. Each VLAN behaves as a separate entity, which enhances security and reduces congestion by isolating network traffic within segments.
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): NFV decouples network functions from hardware devices and runs them as software on virtual machines. Use cases include virtual firewalls and load balancers, which enhance scalability and reduce hardware dependency.
Comparison & Use cases
Comparatively, NFV is best for service agility and cost reduction, Overlay Networks for scalability and flexibility, and VLANs for traffic management and enhanced security.
In practice, many organizations benefit from integrating multiple types of network virtualization to address comprehensive networking needs. For example, a large enterprise might employ NFV for efficient deployment of network services, and utilize VLANs and Overlay Networks to segment and secure departmental communications. This integrated approach allows businesses to leverage the specific advantages of each network virtualization type, optimizing their networks in terms of both performance and cost.
Network Virtualization Software
The landscape of network virtualization software is diverse, featuring renowned network virtualization platforms such as Cisco ACI, Microsoft Hyper-V, VMware NSX, and Sangfor HCI, each offering noteworthy solutions.
- Sangfor’s HCI offers a comprehensive and effective solution, integrating virtualized networking, computing, and software-defined storage. Designed for scalability, it expands capacity as your organization grows. Sangfor HCI is recommended for organizations seeking a complete solution for network virtualization and management.
- Cisco ACI offers comprehensive management of multi-cloud environments, emphasizing scalability and network optimization for businesses expanding into cloud-based operations.
- Microsoft Hyper-V is a user-friendly hypervisor that effectively virtualizes hardware products. While it may lack some advanced features found in more complex hypervisors, it remains a solid choice for organizations seeking straightforward management and deployment.
- VMware NSX excels in providing advanced network segmentation, fine-grained security policies, and automated disaster recovery solutions, making it an ideal choice for organizations prioritizing robust security and agile response capabilities.
- The Array AVX Series is a versatile, enterprise-level solution tailored for MSPs, featuring customizable options to fit various workflows. As a comprehensive platform, it offers streamlined management through a unified toolset, providing an effective and cohesive solution.
Network Virtualization in HCI: Why Sangfor?
Sangfor HCI excels by integrating advanced features into a cohesive, user-friendly platform, enhancing security and making network management more intuitive. Its focus on easy deployment and compatibility with existing infrastructure ensures a smooth transition to virtualized networks, minimizing disruptions.
Network virtualization within Sangfor’s Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI) enhances the overall efficiency and scalability of IT operations. Sangfor HCI combines compute, storage, and networking into a single system, simplifying resource management and reducing operational costs.
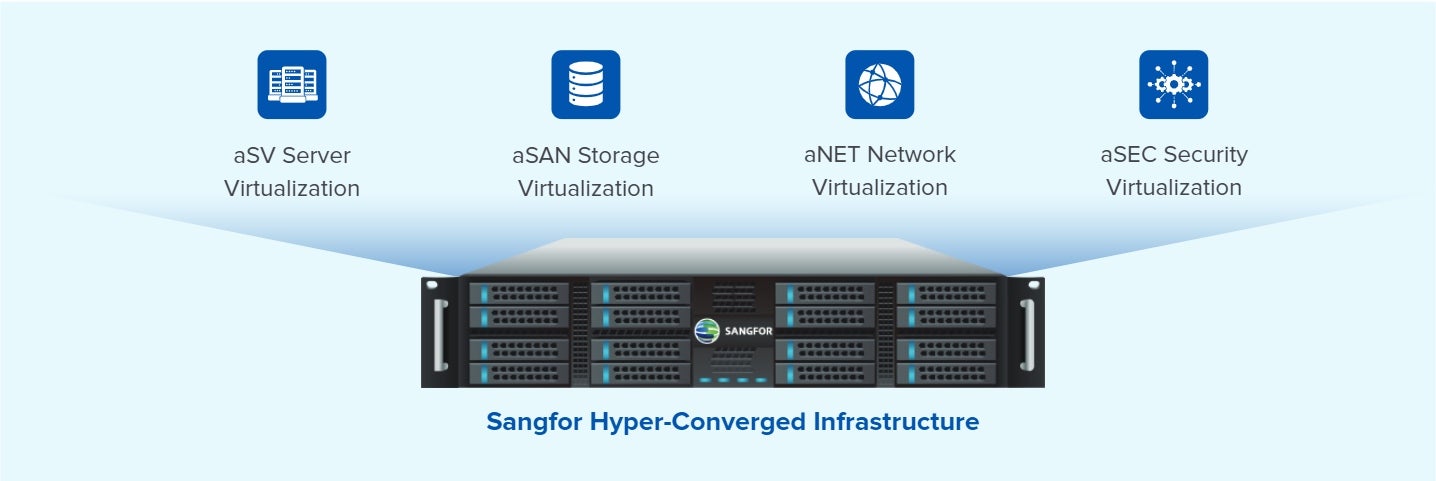
Illustration of Sangfor Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI)
The benefits of Sangfor HCI include streamlined deployment, improved network oversight, enhanced security, and dynamic resource allocation, making it a strong choice for businesses looking to optimize their network operations. Additionally, its capabilities in disaster recovery further enhance its appeal, positioning it as an ideal solution for businesses aiming to maximize network virtualization efficiency and scalability.
For more detailed information on how you can leverage network virtualization with Sangfor Technologies, visit Sangfor HCI.
Embrace the Future with Network Virtualization
Looking ahead, network virtualization is poised to become even more integral to IT infrastructure strategies, with advancements likely to focus on even greater automation, AI integration, and enhanced security protocols.
As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, the strategic adoption of network virtualization will thus become essential. For those ready to leverage these technologies, Sangfor HCI offers a robust, streamlined gateway to network virtualization. Embrace the future of networking today with Sangfor and enhance your operational capabilities.





