The creation of Artificial Intelligence has been one of the fundamental hurdles in digital transformation in the last century. Since its inception in the 1950s when machines were only challenged to beat someone in a chess match, the AI revolution has expanded greatly to allow machines to adapt, learn, and process on a level matching – and sometimes exceeding – human thought. Today, AI computer systems can easily replicate human behavior and thinking patterns using machine learning algorithms to form rules. However, with great power comes great responsibility – and great consequences.
This blog article focuses on AI hacking and how AI cyber-attacks have risen tremendously since the mainstream use of the technology. We look at how AI can be used to commit cybercrime, the emerging AI threats, and how AI can help hackers target people. We also look at specific AI scams that are used and how to use AI wisely to prevent cyber-attacks instead. First, let’s get a brief understanding of how AI cyber-attacks became more popular.
The Rise of AI-Based Cyber-Attacks
The AI cyber-attack pandemic is far from a discovery and the potential for such disastrous consequences has been predicted early on by many cybersecurity experts. AI allows threat actors to automate and simplify hacking processes – making it an easy route for novices and newcomers in the field. The rise of AI in most mainstream products has undoubtedly made it one of the most coveted technologies for companies. This has pushed AI developers to produce more models in a shorter period. However, with vested commercial interests, these developers might ignore potential risks.
A recent report from the UK’s National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) confirms that AI will “almost certainly increase the volume and heighten the impact of cyber-attacks over the next two years.” The same report also states that AI has opened up the field of hacking to opportunistic cyber criminals who might not have the skills to orchestrate a cyber-attack alone. This means that AI is making hacking more accessible and easier to use – encouraging hackers to turn to AI technology to do or supplement their hacking.
In another video interview with Information Security Media Group at the RSA Conference 2024, JC Raby, the managing director and head of emerging technology at JP Morgan Investment Banking discussed emerging market threats. He noted that AI only threatens to accelerate those threats given that you can mount a full-scale attack using several attack surface management visibility. With AI seemingly here to stay, organizations need to be aware of how it can be used against them to commit cyber-attacks and steal data.

How Is AI Used for Cybercrime?
AI is a complex technology that grows and can be fed each day. This means that computer systems can be trained to complete tasks as needed. However, without any moral persuasion, these systems can also then be taught to carry out cyber-attacks. One of the ways that AI can be used is through the use of Generative AI technologies. These are AI models that can generate new content – including text, images, videos, and more. Generative AI has sparked controversy within many fields already and has become a loophole for a lot of companies to exploit and generate content without employing artists or creators.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are an example of Generative AI that is widely used today. Platforms like ChatGPT can easily generate content and answer questions – with inaccuracies most of the time. Most large companies like Google, Meta, iPhone, and more have also taken to using generative AI in their products as well. In terms of cyber threats, at the very least, threat actors can use Generative AI to automatically create convincing emails or documents to lure people into phishing campaigns.
Generative AI can also be used to create malware that can evolve to fix itself as needed to infiltrate a network or exploit a vulnerability. Moreover, AI can be used to create deep fake videos to manipulate people. AI is an innovative tool that can be weaponized to create cyber threats that are self-learning, increasingly persuasive, and worryingly invulnerable. Now, we’ll look further into identifying what an AI cyber-attack is and how it can be used.
What Are AI Cyber-Attacks?
AI cyber-attacks can be defined as any hacking operation that relies on the use of AI mechanisms. An AI hack will use the advanced machine learning algorithms of AI platforms to identify vulnerabilities, predict patterns, and exploit weaknesses in networks. The automated and adaptable nature of AI also makes it possible for threat actors to analyze data and infiltrate systems faster than traditional cybersecurity measures can keep up with. This gives hackers a tactical advantage in their attacks.
An AI cyber-attack has the unique ability to learn where it went wrong and immediately rectify itself – helping it avoid most cybersecurity protocols that exist today. Apart from real-time analysis and adaptability, AI hacking also makes the investigative process a lot more difficult by deleting logs. These are typically used to find “fingerprints” and lead to the threat actors. This makes AI cyber-attacks a formidable threat to cybersecurity. We’ll now explore some of the emerging AI threats and scams seen today.
Emerging AI Threats and Scams
As Artificial Intelligence gains more traction, hackers are starting to weaponize the technology in new and innovative ways. Generative AI has been a cornerstone in these developments with hackers using machine learning systems to orchestrate social engineering attacks and phishing scams by generating plausible emails, documents, and more that inject malware or steal credentials. AI can also be used to mimic human behavior and can be exceedingly difficult to identify for unsuspecting people.
The U.S. Senate Special Committee on Aging released a report to help older civilians detect AI scams that could be used by hackers. The report warns that chatbots will simulate human conversation and could be used by hackers to get personal information. Threat actors can also use deepfakes or voice cloning techniques to imitate trusted people and obtain information or private details. Another example of this is in crypto investment scams that use deepfakes of celebrities to promote their projects and seek investments. Binance’s former CCO, Patrick Hillmann, was the target of AI deepfake scammers in 2022 when they used his likeness in an attempt to defraud potential victims from the crypto industry.
While most Language Learning Models have been able to identify and prevent their platforms from being used to generate malware, hackers still find ways to trick the system into it. This has led to the emergence of hacking platforms like HackedGPT and WormGPT that openly assist threat actors in generating malware. The unethical hacking tools can be used for hacking, carding, identity theft, data exfiltration, and more. To effectively protect yourself from AI hacking, it’s important to understand how AI is used to target people as well.
How Do Hackers and Scammers Use AI to Target People?
AI can be used in several ways to augment and elevate a cyber-attack or social engineering scam. A 2020 report from the Georgetown Center for Security and Emerging Technology looked at the potential use of AI across some of the same activities and identified similar areas of risk. It noted that automation was a major factor for some hackers to turn to machine learning techniques to carry out cyber-attacks. The report also mentions that machine learning has the potential to increase both the scale and success rate of spear phishing and social engineering attacks.
This means that AI is often used to generate false emails, attachments, and messages to lure naïve or oblivious people within a company or unsuspecting individuals into giving away their credentials or unknowingly injecting malware into the network. AI can also be used to detect vulnerabilities in a system within seconds to exploit. This can be done by reversing comparisons between published versions of software to identify what has been patched or by analyzing the open-source code. The speed of AI is a crucial part of this process. Now, we can explore the more specific AI threats in more detail to see how threat actors target people.

AI Hacking Threats
AI hacking threats come in many different shapes and forms. With AI technology constantly learning and evolving to solve more complex problems – or infiltrate more complex security – the number of AI hacking threats we would have to deal with is only expected to grow. For now, we can list some of the main AI cyber attack threats to look out for:
1. Deepfake AI Hacking
Deepfakes are created using generative AI to mimic the likeness of a human. Typically, deepfakes are used for promotional purposes where celebrities, politicians, or other authoritative figures are used to promote a brand or project. A deepfake will use existing video footage, photographs, and voice recordings to create AI-generated video and sound clips. The AI can use face-swapping and facial manipulation to mimic the victim’s facial movements and create seemingly legitimate videos to scam people.
While it might seem like a simple enough scam to trick your grandparents into thinking Tom Cruise wants them to buy an iPhone, deepfakes can affect anyone. Deepfake attacks persuade employees to give up confidential information from seemingly trusted figures. These videos can also be used to spread propaganda and can have serious implications in times of political unrest or uncertainty – causing reputational damage, misinformation, and financial losses. The World Economic Forum reported that 66% of cybersecurity professionals experienced deepfake attacks within their respective organizations in 2022 alone.
2. Generating Malware AI Hacking
Generative AI can be used to create polymorphic malware that adapts and mutates its source code to avoid detection and security protocols. For traditional antivirus systems that use signature-based identification, this can prove to be difficult to defend against. While AI malware generation is trying to be curbed by most platforms, several dark web forums still offer AI-based malware creation.
3. AI Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks focus on manipulating people into giving out their credentials or opening suspicious links and attachments. With the use of AI, hackers can craft automated and efficient social engineering scams to mislead people and gain access to private data.
4. AI Brute Force Attacks
A brute force attack will try to exhaust all password combinations to crack a secured location. With the addition of AI, brute force attacks can be seamlessly automated and allow hackers to analyze user behavior and patterns to figure out passwords faster.
5. AI Hack Phishing
Another common AI hacking threat is increased phishing. These attacks rely on deceiving employees or individuals into thinking that correspondence comes from a legitimate source. AI has streamlined the capabilities of phishing attacks by generating automated and efficient phishing emails that are more personalized – adding to their legitimacy.
This is because AI can observe and pattern the phishing scam according to deep analysis. Harvard Business Review reported that 60% of participants fell victim to AI-automated phishing when compared to non-AI phishing scams. The automation of phishing using LLMs also reduces the costs of the attacks by more than 95% while achieving equal or greater success rates – making it the most attractive option for threat actors.
6. AI CAPTCHA Cracking
CAPTCHA has been used for a long time to root out bots on the Internet and determine if a user is a human. However, AI has now proven to be better at solving CAPTCHA forms by analyzing images and choosing according to human behavior patterns learned.
7. Voice Cloning AI Hacking
As much as visual deepfakes can be troublesome, voice cloning can be equally dangerous in the wrong hands. Voice biometrics is quite a common security measure for many devices and systems. AI can now duplicate audio fingerprints and mimic voice clips off sample vocals. This means that voice-protected systems are vulnerable and people can be deceived into thinking an audio file is legitimate when it’s not – enabling hacking, misinformation, and identity theft.
8. AI Keystroke Listening
Another way that AI can be a threat is through listening to keystrokes. Some AI tools can actively record the different keys you type into your keyboard to steal passwords with almost 95% accuracy.
All these AI threats can be used in different ways to steal data and credentials. While these methods might seem far-fetched, AI hacking will rely on nonchalance to thrive. To truly understand the effects and ramifications of AI cyber-attacks on the state of cybersecurity, let’s explore some sobering statistics.
Statistics on AI Hacking and Cybersecurity
When it comes to AI in cybersecurity, many companies and developers will rush to cover their bottom lines before configuring effective protection for AI tools. The threat that AI poses to cybersecurity cannot be ignored any longer and organizations have a responsibility to educate themselves and their employees on the risks of AI cyber-attacks. While AI hacking can be difficult to spot and remediate, it is imperative to know how AI hacks have transformed the cybersecurity landscape into an unsteady playing field. Here are some of the statistics that should be used to inform your stance on AI cyber-attacks:
- The global market for AI-based cybersecurity products is estimated to reach $133.8 billion by 2030, up from $14.9 billion last year. (CNBC)
- As much as 90% of online content may be synthetically generated by the year 2026. (WeForum)
- Businesses affected by AI-powered scams often endure not just direct financial losses but also face erosion of customer trust and potential legal ramifications. (2024 Sophos Threat Report)
- The use of AI in the UK will almost certainly make cyber-attacks more impactful because threat actors will be able to analyze exfiltrated data faster and more effectively and use it to train AI models.
- 75% of security professionals witnessed an increase in attacks over the past 12 months, with 85% attributing this rise to bad actors using generative AI. (SecurityMagazine)
- Around 48% of IT decision-makers are not confident they have the technology in place to defend against AI attacks. (Forbes)
- Only 52% of IT decision-makers expressed high confidence in their ability to detect a deepfake of their CEO. (Forbes)
- AI lowers the barrier for novice cyber-criminals, hackers-for-hire, and hacktivists to carry out effective access and information-gathering operations. This enhanced access will likely contribute to the global ransomware threat over the next two years. (NCSC)
- Moving towards 2025 and beyond, commoditization of AI-enabled capability in criminal and commercial markets will almost certainly make improved capability available to cybercrime and state actors. (NCSC)
The report from the UK’s National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) also states that AI will almost certainly increase the volume and heighten the impact of cyber-attacks over the next two years. However, the impact of the cyber threat will be uneven.
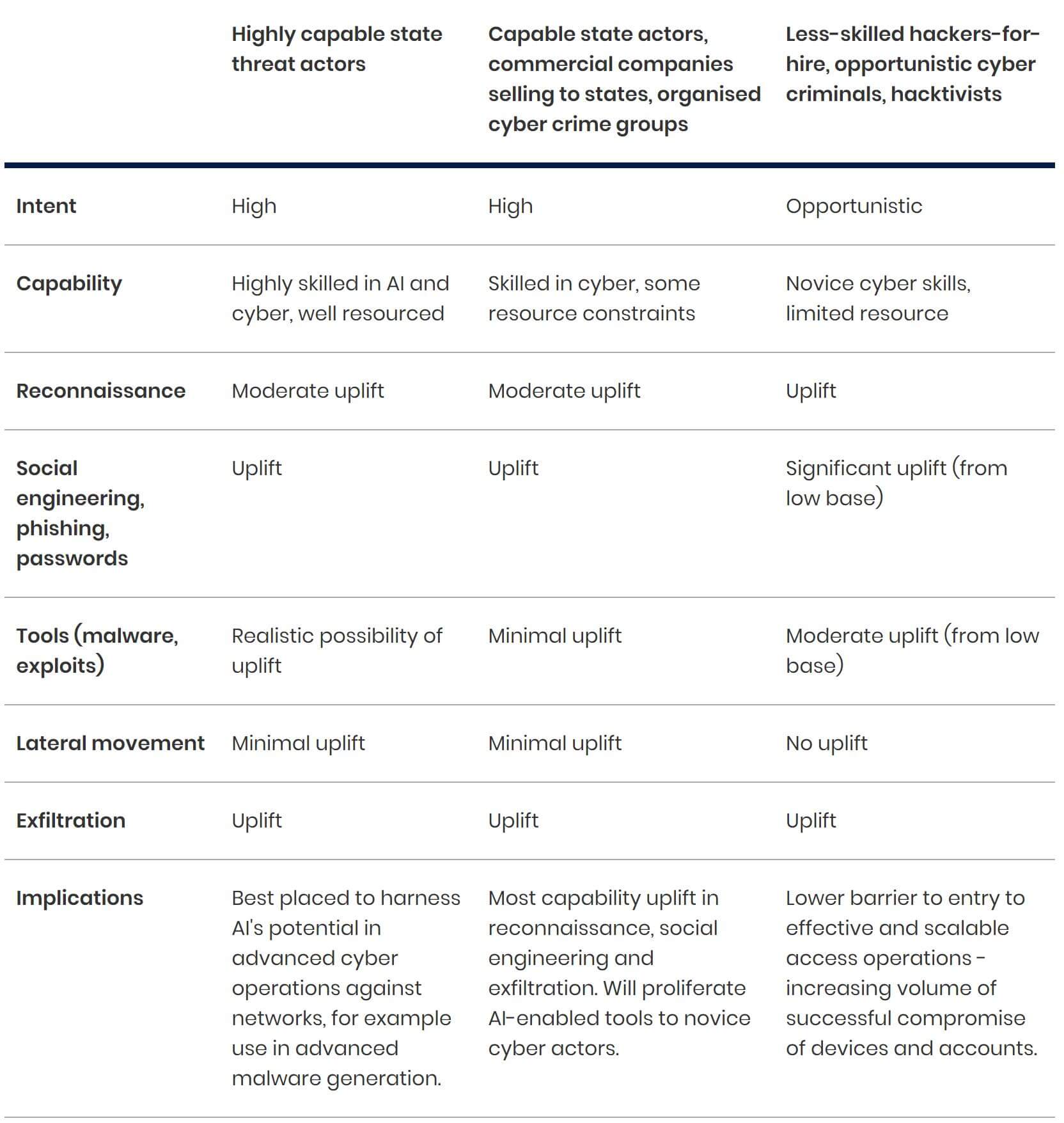
Table 1: Extent of capability uplift caused by AI over the next two years.
KEY: MINIMAL UPLIFT → MODERATE UPLIFT → UPLIFT → SIGNIFICANT UPLIFT.
Sourced from NCSC.
Another report by Maia Hamin and Stewart Scott maps the existing capabilities of Generative AI (GAI) models to the phases of a cyber-attack lifecycle. This helps to analyze whether and how these systems might alter the offensive cyber landscape.
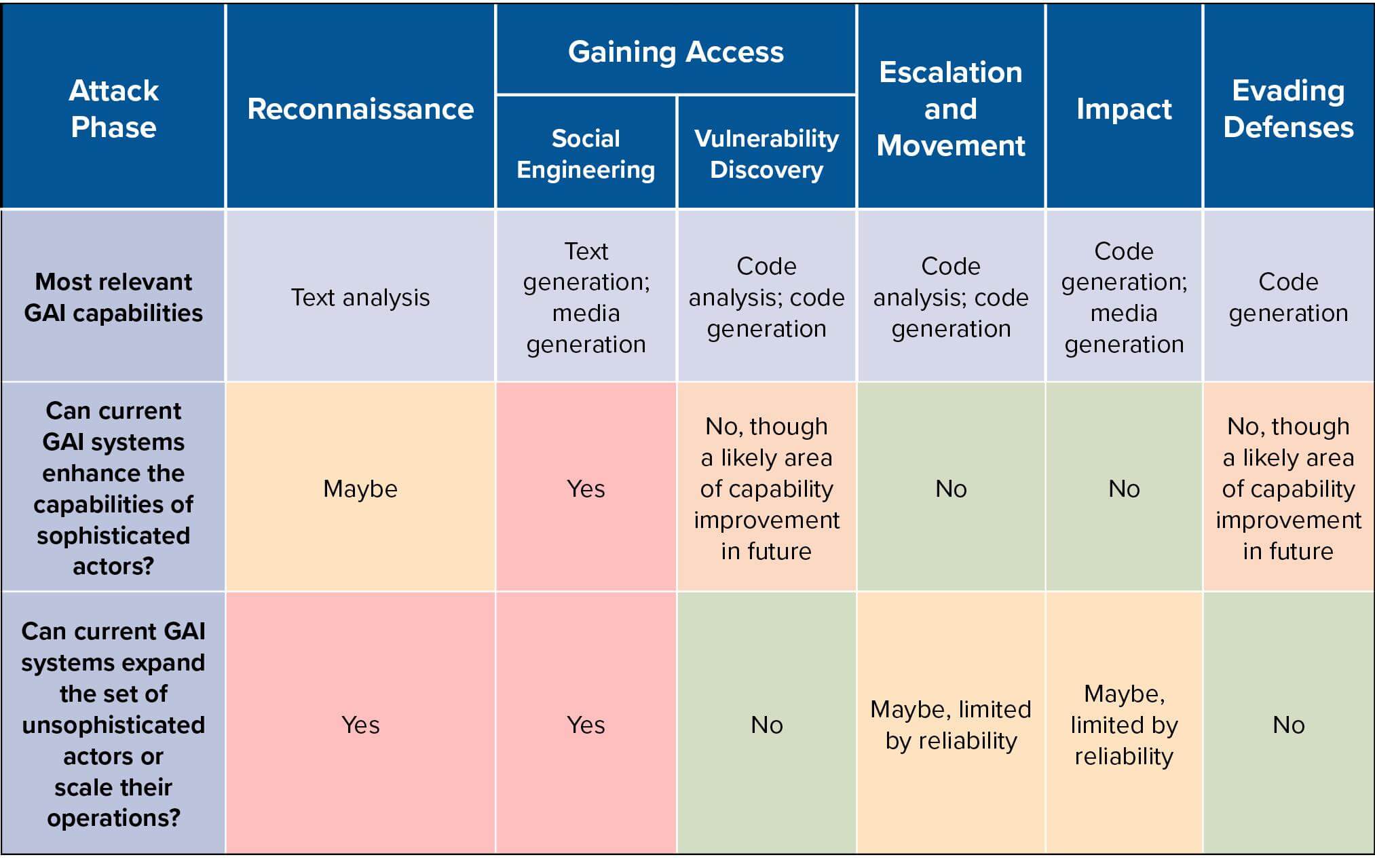
Table 2: Overview of relevant GAI capabilities and level of capability enhancement across different phases of the cyber-attack lifecycle. Sourced from Hacking with AI report
While there is no evidence yet that LLM systems can complete multiple phases of an entire cyber-attack without human intervention, several factors demand ongoing attention to this question. This involves looking into the way that the unsupervised learning paradigm creates capabilities overhang as well as increasing focus and development energy around autonomous systems. To address these challenges, the report also concludes with policy recommendations for AI systems. These include:
- Developing testing standards for leading-edge models that assess cyber risks across different phases, actors, and levels of autonomy, prioritizing transparency, and participation.
- Assessing and managing cyber risks arising from GAI systems while protecting the equities of open model development.
- Mobilizing resources to speed up technical and standards-setting work on AI content labeling with a focus on implementation potential.
- Investing in policy structures and technical measures to address potential risks associated with AI-based autonomous agents.
Limiting AI misuse is a massive cybersecurity issue and needs to be treated as such. A recent Executive Order on AI from the Biden administration points governments in the right direction by requiring that developers and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) providers make reports to the federal government related to the training of “dual-use foundation models,” defined in terms of their potential capability to pose serious threats to national security such as through enabling automated offensive cyber operations.
Sticking to the mantra of fighting fire with fire, the greatest development in the fight against AI hacking has ironically been the use of AI-Powered Cybersecurity Solutions. Artificial Intelligence has proven to be crucial in creating cybersecurity solutions that can predict, detect, and eliminate cyber threats in real-time with reduced expenses and impressive accuracy. The same automated capabilities that make AI hacking a breeze can be used to analyze large data sets for anomalies.
Sangfor uses AI in several cybersecurity platforms to streamline processing, automate tasks, and provide enhanced testing and monitoring solutions. The Sangfor Cyber Command platform uses an enhanced AI algorithm to monitor for malware, residual security events, and future potential compromises in your network. It’s also coupled with advanced Threat Intelligence technology to keep you updated on any vulnerabilities detected.
Additionally, Sangfor’s Endpoint Secure technology uses an AI Detection Engine and provides integrated protection against malware infections and APT breaches across your entire organization's network. In the right hands, AI can be a strategic cybersecurity tool and will ultimately protect your organization best in a time when AI hacking is on the rise. Despite the several ways AI cyber-attacks can be weaponized, it’s important to invest in technologies that can truly be effective in an evolving digital climate. Safeguard your future and contact Sangfor Technologies today to see how we can wield AI to keep you protected.
People Also Ask
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cybercrime is a tool that can be used to predict patterns, analyze data, and automate tasks within cyber-attacks or can be used to elevate cybersecurity platforms.
AI attacks are cyber-attacks in which AI has been the main tool used.
Hackers can use AI to:
- Generate malware
- Create deepfake videos
- Create phishing emails and scams
- Conduct social engineering attacks
- Crack CAPTCHA forms
- Listen to keystrokes
- Assist in brute force attacks
Most hackers will use AI tools to analyze large amounts of data to search for private information or credentials. They can also use it to generate malware, phishing scams, and deepfake content, or to automate hacking tasks.





