ZSand Product Overview
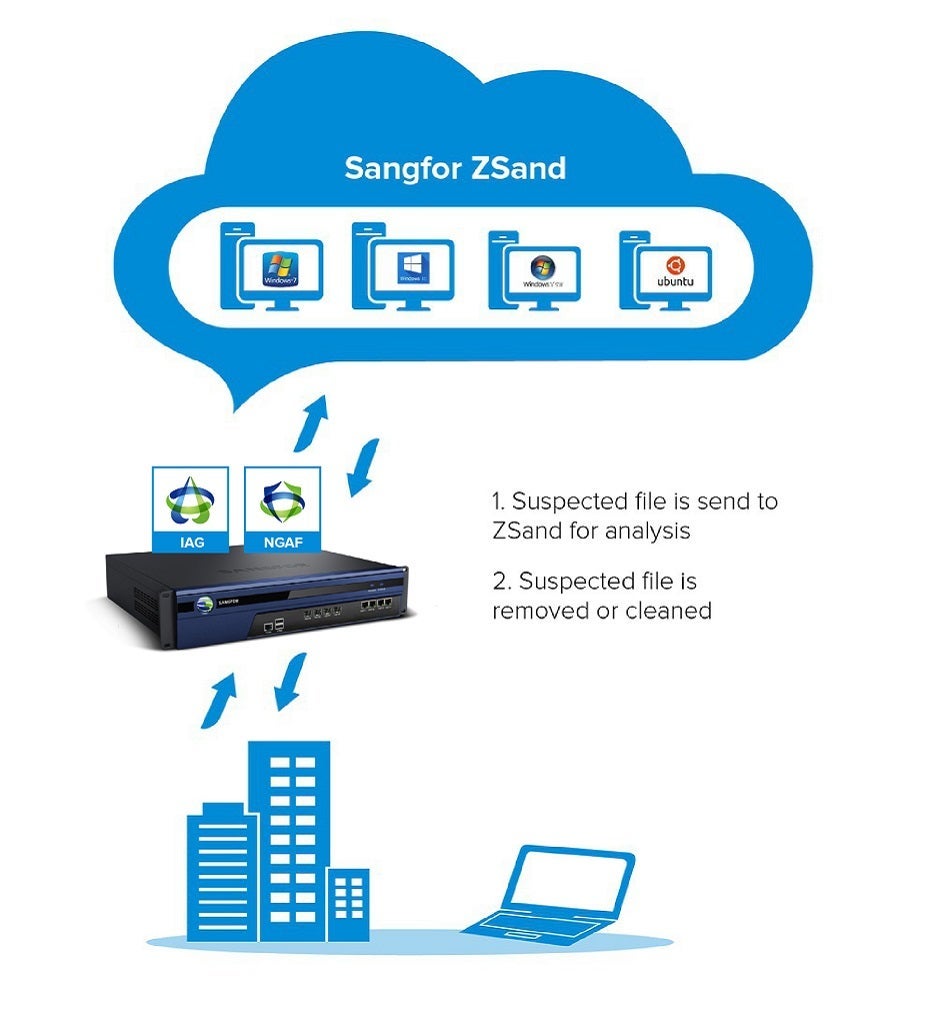
Sangfor's ZSand is sandboxing technology designed to detect previously unknown malware. Suspicious files are captured by Sangfor’s NGAF and sent to ZSand for processing. ZSand contains a set of safe virtual environments that mimic an actual victim’s OS, files and applications. The suspicious files are then executed or detonated in this controlled environment where behaviours such as file access, registry edit, process and network activities can be monitored and analysed.
Sandboxing then shares relevant IOC and malware behaviour report with Neural-X’s Threat Intelligence. Neural-X uses this data to enhance its analysation capability, eliminating the need for a second round of sandboxing and providing timely protection to customers who are connecting to Neural-X via network and endpoint solutions. Customers, security researchers and botnet researchers benefit from the vast amount of real-time data, making the business of network security proactive and exponentially more effective.
ZSand supports executable files and scripts in both Windows and Linux operating systems. In recent tests, it has accurately detected ransomware families including GandCrab, Zusy, GlobeImposter, and LockCrypt.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the world of cybersecurity, a sandbox is an isolated, testing field on a network that mimics end-user environments. It is a safe space for users to experiment with and inspect different variables without risking harm to the hosting device or network. Sandboxing is an additional layer of protection against zero-day threats and to avoid system failures.
With an advanced sandboxing solution like ZSand that creates detailed behavioral reports, users can monitor and analyze activities of abnormal files captured by security detection solutions like NGAF. It works in both Windows and Linux operating systems.
When combined with a robust security solution like Neural-X, sandboxing provides timely protection for networks and endpoints against malware with real-time data.
Sandboxing is an approach that proactively identifies malware by executing suspicious files, codes or URLs in a restricted, virtual environment independent of your computer and network. The typical security detection workflow of a sandboxing operation goes by the following steps:
- The “sandbox” receives a request to scan or run an object (URLs, programs or files), with detailed instructions including but not limited to OS and configurations, test time limits, information on other software installed and so on.
- The test object is run while a cyber threat intelligence in the sandbox collects artifacts and records the object’s interaction with other known security threats.
- The sandbox analyzes the artifacts collected and adds the object’s data to the verdict for future analysis. If a suspicious event is found during the execution of sandboxing, a detailed description will be sent back to the user.
The major benefit of harnessing sandboxing as a measure to improve your organization’s security, is its isolated nature. Sandboxing is the safest way of security detection without compromising any operating systems, hosting devices, or in other words, your daily operation. It also offers an extremely-high security detection rate along with a function to remove harmful threats proactively.
Sandboxing is often seen as a complement to existing cybersecurity products and policies. By investing in solutions with a sandboxing function like Neural-X, you get an all-around security solution that includes a wealth of security detection strategies. Neural-X safeguards your system and network with near immunity to all cyber attackers’ invasion techniques.
