1. Overview of BabLock Ransomware
| Malware Family | BabLock (aka Rorschach) |
|---|---|
| Threat Type | Ransomware |
|
Description |
The BabLock ransomware has been observed to spread by exploiting an email application vulnerability and uses a multi-component package to perform encryption. This ransomware family implements one of the fastest encryption speeds ever observed. |
2. Analysis of BabLock Ransomware
2.1 Introduction
Sangfor FarSight Labs recently captured a sample of a new ransomware family that shares many characteristics with other ransomware families, such as Lockbit 2.0 and Babuk. We identified the sample as belonging to the Bablock ransomware family which is also known as Rorschach. According to samples submitted to VirusTotal, BabLock has been responsible for attacks in Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. In one of the attacks, the threat actors exploited the now-patched arbitrary file upload vulnerability in Zimbra Collaboration (ZCS) 8.8.15 and 9.0, identified as CVE-2022-41352, to remotely execute arbitrary code.
When the ransomware is launched on a domain controller with administrator privileges, it can spread across the local area network by creating a Group Policy Object (GPO).
The attack chain of the ransomware is as follows:

2.2 Analysis
2.2.1 MITRE ATT&CK
| Tactic | Technique | Sub-Technique | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Access (TA0001) | (T1190) Exploit Public-Facing Application | N/A | Exploit arbitrary file upload vulnerability in Zimbra Collaboration |
| Execution (TA0002) | (T1059) System Service | (T1059.003) Command and Scripting Interpreter: Windows Command Shell | Use a series of Windows commands, such as bcdedit.exe and net1.exe |
| (T1047) Windows Management Instrumentation | N/A | Use WMIC to delete shadow copies | |
| (T1106) Native API | N/A | Use direct system calls (syscall) to access system API functions | |
| (T1574) Hijack Execution Flow | (T1574.002) DLL Side-Loading | Use a legitimate .exe program to load a DLL | |
| Defense Evasion (TA0005) | (T1562) Impair Defenses | (T1562.004) Disable or modify system firewalls | Turn off or disable system firewalls |
| (T1562.001) Disable or modify tools | Terminate the antivirus software Defwatch.exe | ||
| (T1497) Virtualization/ Sandbox Evasion | (T1497.002) User Activity Based Checks | Execute the encryption operation only when the value of the --run parameter is correct | |
| (T1140) Deobfuscate/ Decode Files or Information | N/A | Decode the ransomware payload prior to execution | |
| (T1070) Indicator Removal | (T1070.001) Clear Windows Event Logs | Clear Windows event logs related to applications, security, system and PowerShell | |
| (T1070.004) File Deletion | Delete related files after the ransomware program is executed | ||
| (T1055) Process Injection | (T1055.002) Portable Executable Injection | Inject the PE file packed using VMProtect | |
| (T1564) Hide Artifacts | (T1564.010) Process Argument Spoofing | Overwrite process memory to hide process command-line arguments | |
| Discovery (TA0007) | (T1057) Process Discovery | N/A | Get information about running processes on the system |
| (T1083) File and Directory Discovery | N/A | Search for specific files, directories, and file extensions targeted for encryption | |
| (T1082) System Information Discovery | N/A | Check the system language | |
| Impact (TA0040) | (T1490) Inhibit System Recovery | N/A | Delete shadow copies, and disable System Restore in Windows |
| (T1489) Service Stop | N/A | Terminate processes and services related to databases, servers, and backups | |
| (T1485) Data Destruction | N/A | Empty the Recycle Bin using the SHEmptyRecycleBinA() function | |
| (T1486) Data Encrypted for Impact | N/A | Encrypt files on the targeted systems |
The compilation time of the ransomware sample was prior to March 2022. As of the publication of this article, there are still 54 mainstream antivirus software vendors whose software or security products cannot identify the BabLock ransomware, whether based on threat intelligence or dynamic and static detection rules.
2.2.2 Analysis of Techniques
Once the ransomware sample is launched, it will immediately delete three related files and then encrypt files in the system. Encrypted files are appended with the extension "k1k2k3", and a random number between 00 and 99 is also added to the end of this extension. After encryption, a ransom note is released to instruct the victim on how to contact the attacker and pay the ransom. The ransom note is named "_r_e_a_d_m_e.txt" and includes the attacker's email address but does not provide information regarding the ransom amount or payment method.
The content of the _r_e_a_d_m_e.txt ransom note is as follows:

Encrypted Files:

The ransomware's execution relies on the following three files:
| File | Function | MD5 |
|---|---|---|
| cy.exe | Legitimate Cortex XDR dump service tool for side-loading winutils.dll | 2237ec542cdcd3eb656e86e43b461cd1 |
| winutils.dll | Ransomware loader to decrypt and inject ransomware shellcode into notepad.exe | f02ff25c2169c6575bdf3cd6f120c324 |
| config.ini | Ransomware application encrypted with RC4 | 57880c0d50028600ed9557a1cb1f60f2 |
Since winutils.dll is compressed using a modified version of UPX 3.96, it cannot be unpacked with a standard version of UPX and needs to be unpacked through dynamic debugging.
Information Collection
1. Collect System UUID
UUIDs are used to identify infected computers so that attackers can track and manage them.

2. Check System Language
Use GetSystemDefaultUILanguage and GetUserDefaultUILanguage to determine the country or region code of the system based on the default language of the system or user. This is used to avoid encrypting the machines that are located in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS).
| Language Identifier | Country |
|---|---|
| 0x042b | Armenia |
| 0x042c | Azerbaijan |
| 0x043f | land |
| 0x082c | New Caledonia |
| 0x0419 | Russia |
| 0x0422 | Belarus |
| 0x0423 | Moldova |
| 0x0428 | Georgia |
| 0x0437 | Liechtenstein |
| 0x0440 | Luxembourg |
| 0x0442 | Monaco |
| 0x0443 | Morocco |
| 0x0819 | Tajikistan |
| 0x0843 | Uzbekistan |
Defense Evasion
1. Fixed Startup Parameters
The ransomware will execute encryption only when the value of the required parameter (—run) is correct.
cy.exe -run=xxxx
--pt=C:\Users\John\Desktop\FileFolder\winutils.dll
--cg=C:\Users\John\Desktop\FileFolder\config.ini
--we=C:\Users\John\Desktop\FileFolder\cy.exe

In addition to the required parameters, this sample also supports the following optional parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
–run=<KEY> |
Four characters. The encryption process will only run when the parameter value is correct |
|
--nomutex=1 |
Whether to create a mutex variable (not created by default) |
|
–path=<PATH> |
The path under which files will be encrypted (all files in the system will be encrypted by default) |
|
–log=1 |
Whether to create a startup log (not created by default) |
|
--nodel=1 |
Whether to delete ransomware files (deleted by default) |
|
--noshare=1 |
Whether to encrypt shared directories (encrypted by default) |
|
–pt=<PT_PATH> |
Path of the legitimate .exe startup file |
|
–cg=<CG_PATH> |
Path of the ransomware payload file |
|
–we=<WE_PATH> |
Path of the DLL file |
|
–diskpart=1 |
Use diskpart.exe to clear the read-only attribute of a disk volume |
|
–hostfile=<HOSTFILE_PATH> |
Path of the Hostfile containing a list of hosts on the LAN (all internal hosts are included by default) |
|
–thread=<N> |
Set the number of threads for encryption |
|
–at=<yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss> |
Set the execution time of the ransomware (executed immediately by default) |
|
--nomail=1 |
Whether to create a ransom note (created by default) |
2. DLL Side-Loading
Use the legitimate software cy.exe to load winutils.dll. The cy.exe (original name: cydump.exe) is a Cortex XDR Dump Service Tool, developed by the cybersecurity company Palo Alto Networks, Inc.

3. Process Injection
Call the following API functions to inject shellcode into the memory of the legitimate process notepad.exe, to execute arbitrary code in the target process. This operation allows the ransomware to bypass de+fense mechanisms such as antivirus software and firewalls.




The ransomware sample launches the notepad.exe in a suspended state and injects shellcode with junk characters at the beginning. Once the junk characters are removed, the shellcode becomes a PE file that is packed using VMProtect. The ransomware writes 64 KB of data to the memory of notepad.exe at a time, as shown in the figure below:
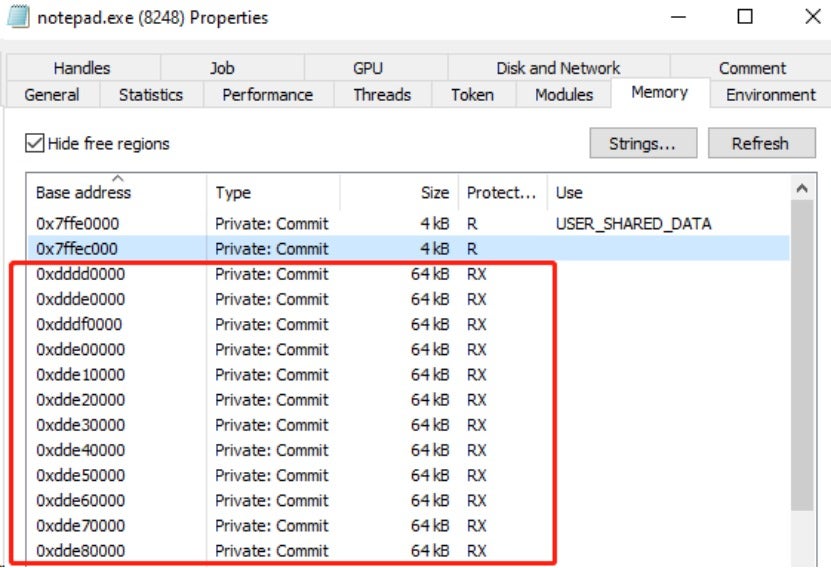
The first 64 KB of data is packed using VMProtect, as shown in the figure below:

4. Process Argument Spoofing
The ransomware launches a system program process in a suspended state, initializes its process environment block (PEB), replaces the command-line parameter with a legitimate one (consisting of the same number of 1s as the length of the parameter being replaced), rewrites the parameter with the real one into the memory using the WriteProcessMemory() function, then, resumes the process, to bypass process memory analysis. For example, the ransowware runs the command "bcdedit.exe /set {default} recoveryenabled no", but the string “/set {default} recoveryenabled no” is replaced with 33 1s before execution, where the string length is also 33.

The following figure shows the real executed commands, which were decrypted through dynamic debugging.

The following describes the commands executed by the ransomware.
(1) Stop services related to databases to prevent file damage or encryption failure, which may occur when the program occupies the files to be encrypted.
- net1 stop MSDTC: Stops the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator service used to manage distributed transactions.
- net1 stop SQLSERVERAGENT: Stops the SQL Server Agent service used to execute SQL Server Agent jobs and manage multiple SQL Server instances.
- net1 stop MSSQLSERVER: Stops the SQL Server database engine service.
- net1 stop vds: Stops the virtual disk service used to manage virtual disks and volumes.
- net1 stop SQLWriter: Stops the SQL Server VSS Writer service used to support the Volume Shadow Copy Service.
- net1 stop SQLBrowser: Stops the SQL Server browser service used to help clients locate the SQL Server instance.
- net1 stop MSSQL$CONTOSO1: Stops the service of the SQL Server instance named CONTOSO1.
(2) Delete system backups and prevent system recovery.
- vssadmin.exe delete shadows /All /Quiet: Deletes all shadow copies.
- bcdedit.exe /set {default} recoveryenabled no: Disables the Windows Recovery Environment.
- bcdedit.exe /set {default} bootstatuspolicy ignoreallfailures: Ignores all boot failures.
- wbadmin.exe DELETE SYSTEMSTATEBACKU: Deletes a system state backup.
- wbadmin.exe DELETE SYSTEMSTATEBACKUP -deleteOldest: Deletes the oldest system state backup.
- wbadmin.exe delete catalog -quiet: Deletes the backup catalog.
- wbadmin.exe delete backup: Deletes backups.
- wbadmin.exe delete systemstatebackup -keepversions:0: Deletes all system state backups.
- wmic.exe SHADOWCOPY /nointeractive: Lacks the required argument “DELETE“. The command to delete a shadow copy is "WMIC.exe shadowcopy delete /nointeractive".
(3) Clear event logs to prevent security personnel from tracing the ransomware’s operations.
- wevtutil.exe clear-log Application: Clears application logs.
- wevtutil.exe clear-log Security: Clears security logs.
- wevtutil.exe clear-log System: Clears system logs.
- wevtutil.exe clear-log "windows powershell": Clears Windows PowerShell logs.
(4) Turn off and disable the Windows firewall, making it easier for attackers to access the victim computer and execute malicious code.
- netsh advfirewall set currentprofile state off: Turns off the Windows Firewall.
- netsh.exe firewall set opmode mode=disable: Disables the Windows Firewall.
5. Use of Direct System Calls (syscall)
The ransomware does not directly call API functions but uses direct system calls (syscall) through specifying the syscall ID. This helps it avoid detection by security software that monitor API function calls.

Impact
1. Terminate Processes
Terminates processes such as databases, servers, remote management tools, hypervisors, and time synchronization program.
wxServer.exe, supervise.exe, sync-taskbar.exe, vxmon.exe, wxServerView.exe, Culture.exe, sync-worker.exe, sqlbrowser.exe, sqlmangr.exe, Defwatch.exe, wsa_service.exe, tomcat6.exe, RAgui.exe, httpd.exe, synctime.exe, Sqlservr.exe
2. Stop Services
Stops services related to the core components of the SQL Server database.
SQLPBDMS, SQLBrowser, SSISScaleOutWorker150, SQLPBENGINE, SQL Server Distributed Replay Client, MSSQLLaunchpad, MSSQLFDLauncher, SQL Server Distributed Replay Controller, SQLWriter, SQLSERVERAGENT, MsDtsServer150, SQLTELEMETRY, MSSQLServerOLAPService, SSISTELEMETRY150, MSSQLSERVER, SSASTELEMETRY,SSISScaleOutMaster150
3. Empty the Recycle Bin
Calls the SHEmptyRecycleBinA() function to delete files in the Recycle Bin to prevent users from recovering files from it.

4. Encrypt Files
(1) Extensions of skipped files

(2) Skipped directories and files

Skips the following directories during the encryption.
bootmgr
AppData
Boot
Windows
WINDOWS
Windows. old
Ahnlab
Tor Browser
Internet Explorer
Google
Opera
Opera Software
Mozilla
Mozilla Firefox
$Recycle.Bin
ProgramData
All Users
BOOTNXT
ntldr
Program Files
Program Files (x86)
#recycle
...
Documents and Settings
Policies
SYSVOL
NETLOGON
scripts
Skips the following files during the encryption:
autorun.inf
boot.ini
bootfont.bin
BOOTSECT.BAK
bootmgr.efi
bootmgfw.efi
desktop.ini
iconcache.db
ntuser.dat
ntuser.dat.log
ntuser.ini
thumbs.db
ntuser.dat
ntuser.dat.LOG1
ntuser.dat.LOG2
AUTOEXEC.BAT
autoexec.bat
config.ini
1_config.ini
begin.txt
finish.txt
_r_e_a_d_m_e.txt
<injected notepad.exe's PID>_l.log
<injected notepad.exe's PID>_e.log
Config.Msi
(3) Encryption
The ransomware utilizes a combination of Curve25519 and HC-128 algorithms, along with I/O Completion Port (IOCP), to achieve multithread encryption.
For each file, a 32-byte private key is generated using the Crypto API function CryptGenRandom.

The encryption process is as follows:
- Creates a ransom note in each directory traversed.
- Determines whether a file needs to be skipped for encryption. If so, the ransomware moves on to the next file. If not, it proceeds with the subsequent actions.
- Uses the Curve25519 algorithm to generate a pair of public and private keys. The public key is used for encryption while the private key is used for decryption.
- Generates a 256-bit HC-128 key and a 32-bit Initialization Vector (IV) for each file, which will used as parameters of the encryption algorithm. These parameters are hardcoded in the ransomware's code.
- Encrypts target files with the HC-128 key and IV generated in step 4. The encrypted HC-128 key is appended to the encrypted files for decryption.
- Append the extension string "k1k2k3(00-99)" to each encrypted file.
2.3 Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| File Name | MD5 |
|---|---|
| cy.exe | 2237ec542cdcd3eb656e86e43b461cd1 |
| winutils.dll | f02ff25c2169c6575bdf3cd6f120c324 |
| config.ini | 57880c0d50028600ed9557a1cb1f60f2 3e3d20f82c4ce395b4a1d1ab60363fc6 cebb3c09bf4bd725ba482822aa1b6e0e 7d0995e365786a0372f61ca25e297ddc |
2.4 Sangfor Solution
The following Sangfor products and services provide protection against the BabLock ransomware:
Sangfor Endpoint Secure
About Sangfor FarSight Labs
Sangfor FarSight Labs researches the latest cyber threats and unknown zero-day vulnerabilities, alerting customers to potential dangers to their organizations, and providing real-time solutions with actionable intelligence. Sangfor FarSight Labs works with other security vendors and the security community at large to identify and verify global cyberthreats, providing fast and easy protection for customers.





