There has been a lot of buzz lately about LockBit ransomware. News of LockBit ransomware attacks has flooded the cybersecurity sphere, causing concern among security teams in organizations and businesses worldwide.
Today, Sangfor FarSight Labs shares insights from our four years of closely monitoring LockBit ransomware to shed light on effective countermeasures.
What is LockBit Ransomware?
LockBit Ransomware is a dangerous ransomware family that steals and encrypts files on a victim’s computer, demanding ransom for decryption. First observed in 2019, LockBit operates as a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), where affiliates deploy the ransomware against targets and share the profits with LockBit operators. Known for its fast encryption speed and ability to evade detection, LockBit targets various sectors, including healthcare, industrial, and financial services.
LockBit ransomware continually evolves, with newer versions introducing more sophisticated encryption methods and evasion techniques, making it a significant threat in the cybersecurity landscape.
The Evolution of LockBit Ransomware
LockBit ransomware first emerged in September 2019 and swiftly caught our attention. It was initially dubbed ABCD ransomware due to the “.abcd” file extension appended to encrypted files. It was renamed to LockBit after the “.lockbit” extension first appeared in February 2020. However, no one could have anticipated that it would evolve into the major ransomware threat it is today.
![]()
The LockBit 3.0 dark web leak site for publishing stolen data. Victim organizations that don’t make the ransom payments have their data uploaded here, available for anyone to download.
From its beginnings as ABCD ransomware to the now-infamous LockBit, this ransomware family has evolved into five distinct versions in just four years.
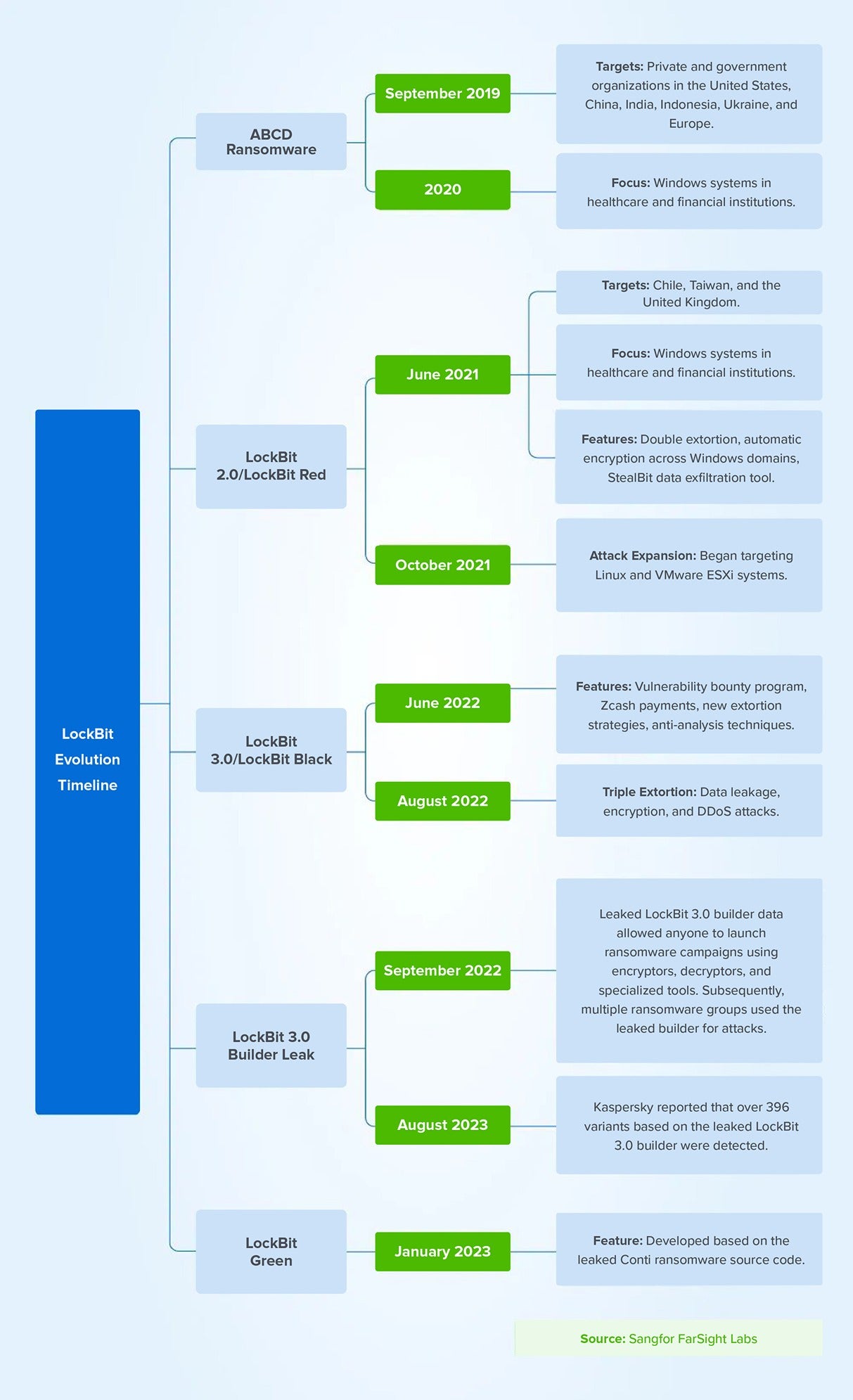
While we won’t delve into the specific technical details of its evolution, it’s important to highlight the rapid advancements of the LockBit group. Their motto, “Making the ransomware great again,” underscores the group’s ambition to innovate and lead in the ransomware landscape. Unlike other ransomware gangs that rely on automated, untargeted attacks, LockBit involves more strategic manual intervention. This leads to more targeted and adaptable attacks with higher success rates.
Moreover, LockBit advocates the Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) model, where affiliates are provided with sophisticated ransomware tools and support to carry out ransomware attacks in exchange for a share of the ransom profits. This approach mirrors a legitimate software company that encompasses everything from development to sales and operations and has matured into a full-fledged industry. The RaaS model, with its lucrative profit-sharing, has attracted numerous criminal groups, rapidly expanding LockBit’s scale. Reportedly, LockBit now has over 100 affiliate groups.
![]()
A UK company was suspected to be a victim of a LockBit attack. LockBit made a cunning offer to extend the deadline for leaking data. For every $10,000 of the ransom demand paid, the deadline is extended by 24 hours, highlighting its sophisticated extortion tactics.
For the LockBit 3.0 version, the ransomware group showcased its grand ambitions by introducing a bounty program, inviting hackers to identify vulnerabilities in their software. This move not only improved their software but also rallied more hackers to their cause. The bounty program has undoubtedly raised the bar in defending against LockBit attacks.
The LockBit Ransomware Kill Chain
Having understood LockBit’s evolution, let’s delve into their attack methodologies.
In essence, LockBit’s attacks can be divided into four stages, each with a clear objective. During the initial access and lateral movement stages, enterprises are often compromised by weak passwords and vulnerability exploits. These are the primary reasons for LockBit’s successful intrusions.
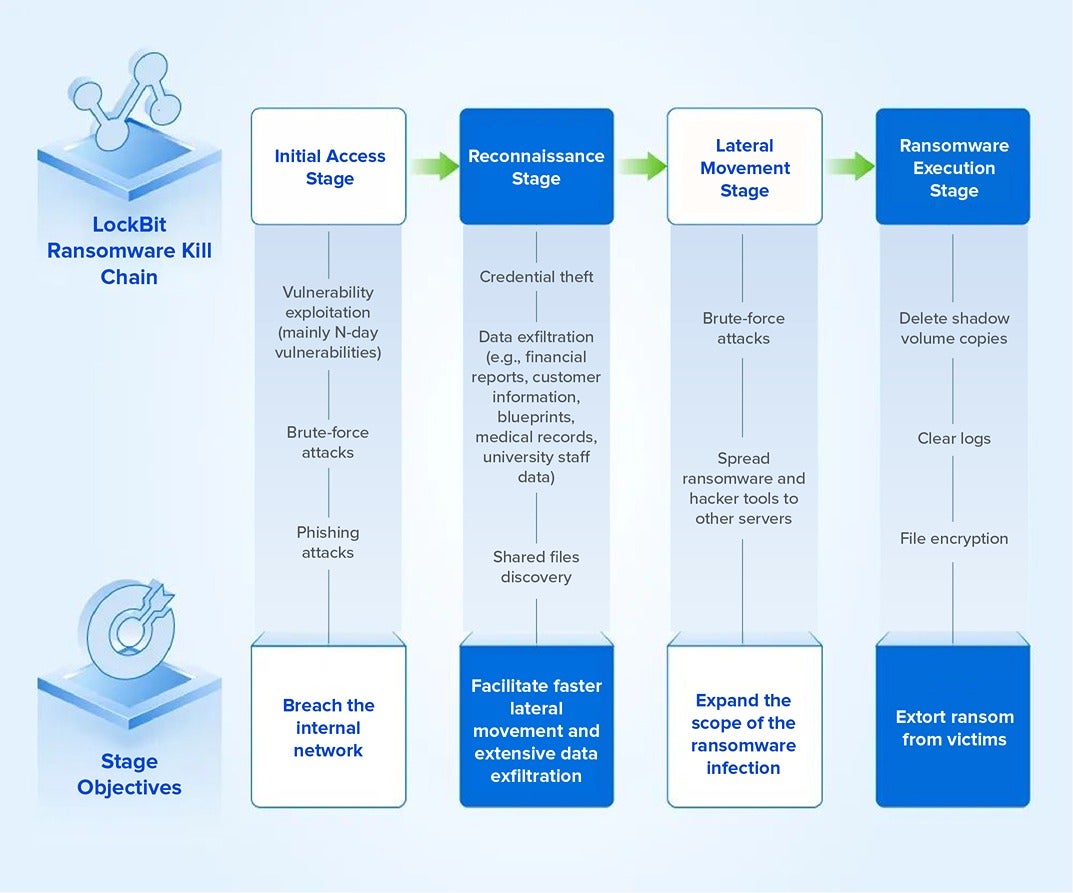
However, what makes LockBit particularly challenging to defend against, and why even large enterprises fall victim, is the human involvement in each stage of an attack. Beyond standard tactics, LockBit attackers constantly adapt their techniques to target the weakest points in a network or device and to evade defenses. While enterprise security awareness is rising, internal vulnerabilities can never be entirely eliminated, making manually operated attacks almost indefensible.
Defending against LockBit Ransomware
Through four years of tracking, we’ve determined that the most critical defensive stage against ransomware is during the execution stage. Disrupting the ransomware during the file encryption process significantly reduces the damage to users.
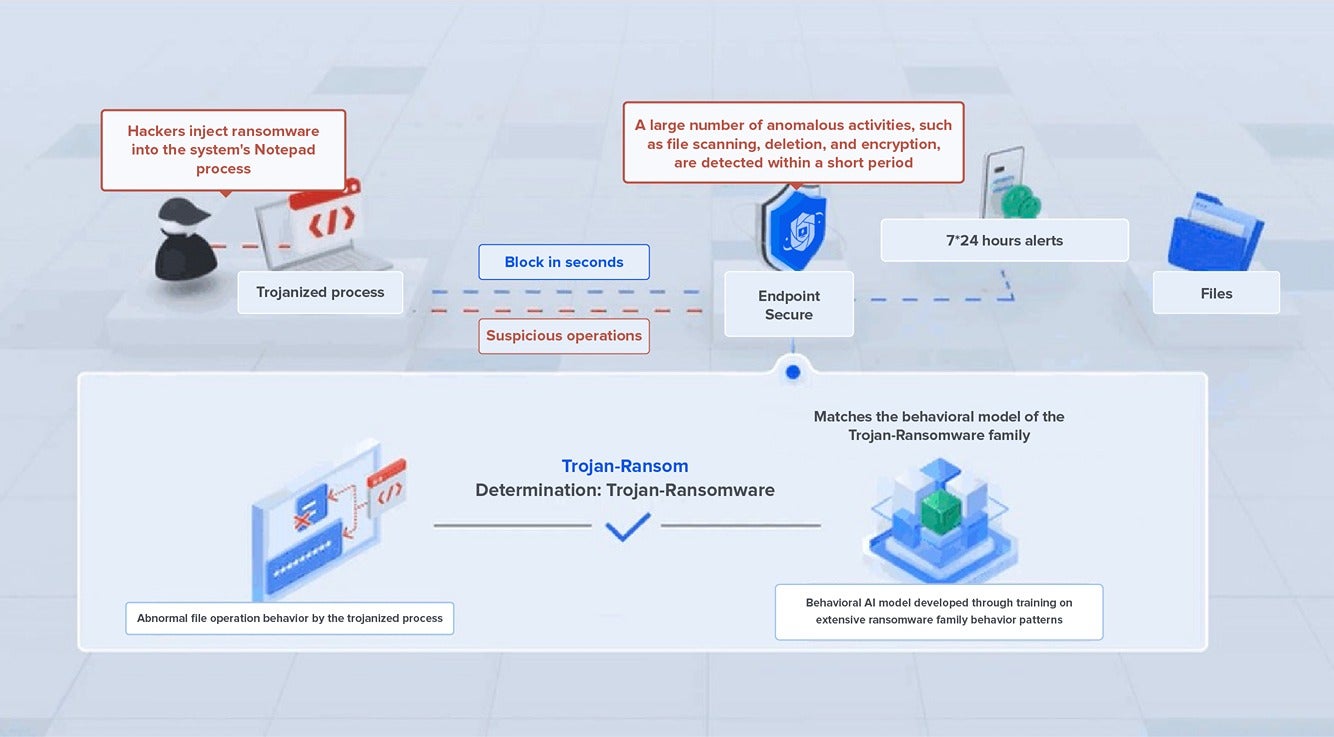
In the case of LockBit, a significant challenge in thwarting ransomware encryption is detecting attacks that use process injection. This technique involves injecting the ransomware’s encryption module into legitimate processes to execute encryption. If the injection is successful, the rapid encryption speed often leaves enterprises unable to respond in time.
Earlier this year, a biopharmaceutical company with Sangfor Endpoint Secure deployed was the target of a LockBit attack. The attackers exploited unpatched vulnerabilities to gain control of multiple servers and attempted to execute the ransomware through process injection.
Fortunately, Endpoint Secure detected and blocked the attack the moment the encryption started. Only a handful of files were encrypted as a result. These files were quickly restored using Endpoint Secure’s file backup recovery feature, preventing any business disruption and data loss.
Sangfor Endpoint Secure’s Key Ransomware Protection Capabilities
Sangfor Endpoint Secure’s ability to detect ransomware attacks in seconds is primarily attributed to the following three key capabilities:
1. Static AI Detection Precisely Detects Ransomware Variants
This year, the Sangfor Engine Zero malware detection engine received an upgrade to boost its AI generalization capabilities. This enhancement enables multi-layered AI detection of suspicious files, improving the detection of unknown threats. It can accurately identify LockBit ransomware and its various strains.

Through AI training, Sangfor Endpoint Secure achieves a 99.83% accuracy in detecting ransomware (data from internal evaluation by Sangfor FarSight Labs).
2. AI Dynamic Behavior Detection Engine
Faced with ransomware families like LockBit, known for using process injection attacks, Sangfor has pioneered a Ransomware AI Dynamic Behavior Detection Engine.
This engine monitors the real-time behavior of both standard system processes and trusted business-related processes, continuously assessing if they exhibit suspected ransomware activities. It identifies various suspicious actions (such as registry modifications, command executions, file releases, and process creations), analyzes them against different ransomware family attack patterns, and builds a ransomware attack kill chain.
If a corresponding attack pattern is detected at the endpoint, Endpoint Secure can kill the ransomware in 3 seconds to contain the spread of encryption.
3. Dynamic Backup Mechanism for Ransomware Recovery
Sangfor Endpoint Secure employs an intelligent data backup mechanism that integrates seamlessly with the Ransomware AI Behavior Detection Engine to trigger backups when required.
Backup options include file backup and snapshot-based (Windows VSS) backup. Both of them allow users to return quickly to operations without data loss when hit with ransomware.

Thanks to these three capabilities, we have successfully prevented hundreds of real-world ransomware incidents for our customers. Notably, the Ransomware AI Behavior Detection Engine has effectively shielded against 90% of ransomware attacks involving process injection. In this year’s SKD Labs tests, Endpoint Secure achieved an impressive 100% ransomware detection rate on both Windows and Linux platforms, setting a new benchmark in its product category.
Sangfor Anti-Ransomware Solution
While ransomware attacks are executed at the endpoint, effective protection requires a holistic approach, as relying solely on endpoint protection is not enough to eliminate risks. Based on the Sangfor XDDR (eXtended Detection, Defense, and Response) framework, we have developed a comprehensive Anti-Ransomware solution. It offers organizations big and small a modular, robust anti-ransomware capability that can be tailored to their needs.
![]()
Core to Sangfor Anti-Ransomware is the integration between Endpoint Secure and the new Network Secure advanced firewall. Network Secure can detect suspicious activity like a workstation attempting to connect to a command & control server. Once detected, Network Secure will direct Endpoint Secure to run local scans to see if an infection or breach has occurred. If so, Network Secure can direct Endpoint Secure to microsegment and disconnect from the network to prevent lateral spread.
Other components of the Anti-Ransomware solution include Cyber Command for threat hunting and SOAR, Cyber Guardian MDR for managed services, and HCI for backup. The integration of each component in the 3 Seconds to Kill Ransomware solution covers one or more steps in the ransomware attack kill chain, ensuring rapid detection and response and always-on threat hunting, providing complete protection against ransomware and APTs.
LockBit Ransomware Risk Mitigation Strategies
With LockBit ransomware becoming increasingly rampant, if you’re concerned about being at risk, consider implementing the following four risk mitigation strategies to reinforce your defenses.
1. Weak Password Check
Review the strength of passwords for RDP servers and databases. Avoid using the same password for multiple devices within the local area network (LAN). Do not expose RDP or database ports directly to the internet to prevent brute-force attacks. Use strong passwords wherever necessary.
2. File Check
Examine the sharing or mapping status of server disks. Set reasonable access permissions for critical files, disable unnecessary file-sharing functions, apply proper access controls to shared directories, and regularly back up business data off-site.
3. System/Software Version Check
Regularly update and patch operating systems and software applications. Outdated systems are often vulnerable to exploits that ransomware like LockBit can capitalize on. Implement a robust patch management process to keep track of updates and apply them without significant delays.
4. High-Risk Port Check
Assess the necessity of open high-risk ports. If necessary, configure source IP access restrictions or other effective control measures.
Conclusion
Having dealt with countless cyber threats for many years, we would like to share a candid insight: There are no 100% secure systems in the world. Cybersecurity is a best effort. It’s about constantly moving closer to safety while reducing any opportunities for malicious actors as much as possible.
Sangfor Technologies remains dedicated to accompanying everyone on this cybersecurity journey. We’re committed to consolidating our experience in combating cyber threats and empowering our products with this knowledge to ensure our customers are always a step ahead.





