The idea of Grid computing came into play based on the concept of Data Processing. Data processing is the core of IT infrastructure. To keep companies running smoothly and operations on track, computers need to be functioning optimally. Processing tasks need to be streamlined efficiently to keep the wheels turning.The architecture is based on the connections made in an electrical grid that all function together to work.
What Is Grid Computing?
Grid computing is a network infrastructure in which all the computer resources are shared amongst a distributed number of computers. These computers essentially pool resources and team up to take on tasks. Within a grid computing model, each personal computer runs its tasks and is loosely linked by the internet or low-speed networks. These computers can be in various locations but are all connected through the control node – or grid server.
The idea behind grid computing is to make use of idle or unused processing power and resources. The grid software is what allows the grid computing infrastructure to connect the network of devices and gives it the directions to work.

What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the outsourcing of processing power, storage, and computing. Instead of buying and maintaining physical servers, companies can make use of only the necessary resources online from a cloud provider. Organizations can use a cloud platform for several resources. These include data backups, disaster recovery, analysis, virtual desktops, and more. With cloud computing, companies can avoid the expenses, complexity, and stress of building their servers.
Grid Computing vs. Cloud Computing
While both grid and cloud computing help to streamline processes, they do have some key differences. Here are some of the main differences between both computing model:
| Grid Computing | Cloud Computing | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost |
No payment is necessary after setup. |
Users have to pay to use the cloud computing platform as a service. |
| Scalability |
Less scalable. |
Extremely scalable. |
| Architecture |
Follows a distributed computing architecture. |
Follows a client-server computing architecture. |
| Resources |
Resources are managed collaboratively. |
Resources are centrally managed. |
| Operation |
Uses a decentralized management system. |
Centralized management system. |
| Ownership |
Grids are owned and managed by the organization. |
Cloud servers are owned by cloud infrastructure providers. |
| Flexibility |
Less flexible. |
More flexible. |
| Accessibility |
Less accessible as it can only be accessed using grid middleware. |
Highly accessible as it can be accessed using conventional web protocols. |
| Services |
Uses systems like distributed computing, distributed information, and distributed pervasive. |
Uses services like Infrastructure-as-a-Service, Platform-as-a-Service, and Software-as-a-Service. |
Examples and Applications of Grid Computing
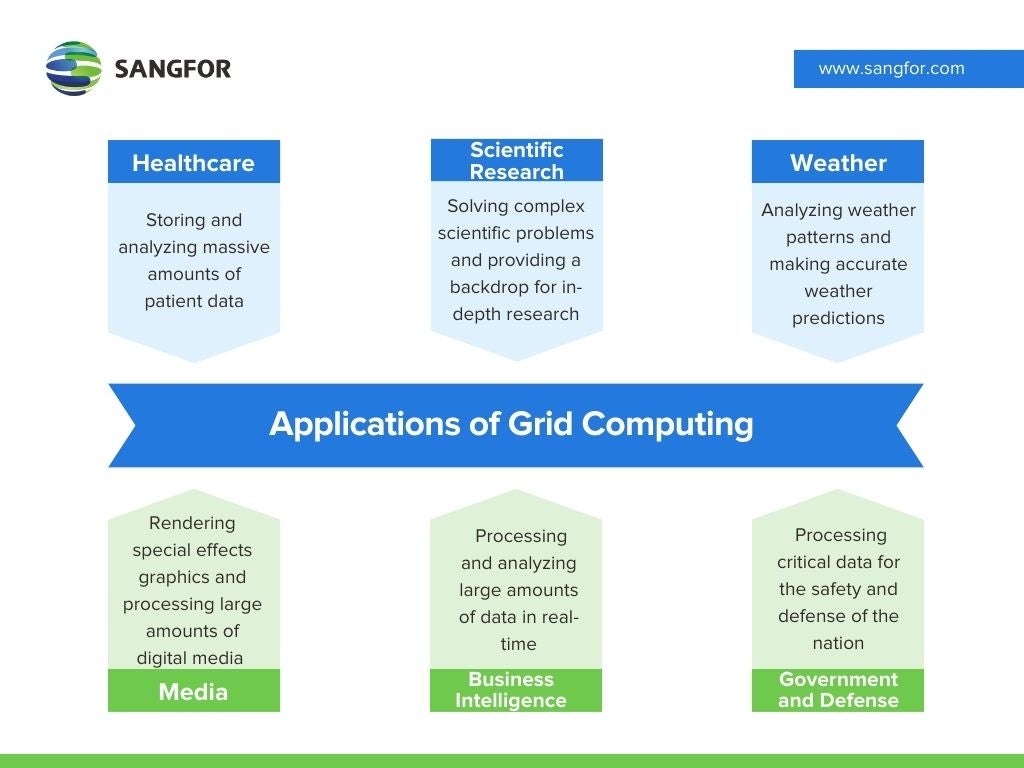
Grid computing presents several advantages. These include better processing power, improved resource utilization, and reduced costs. By using multiple computers, companies can tackle larger, more complex tasks while making full use of their resources. It has been helpful across multiple industries. Some of its applications include:
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, grid computing has been used to store and analyze massive amounts of patient data. The storage and analytic capabilities are also useful in medical developments, research, and improvements.
- Scientific Research: Grid computing can be used to solve complex scientific problems and provide a backdrop for in-depth research. Data can be used to create simulations, models, and analysis reports that can further our scientific understanding in the fields of physics, biology, chemistry, and more.
- Weather: Weather forecasts need large amounts of data and analysis. Meteorologists can use grid computing to analyze the data from different computer locations within the infrastructure and combine the results. This can help to analyze weather patterns and make accurate weather predictions.
- Media: When making a movie, grid computing can be used to speed up production by rendering special effects graphics and processing large amounts of digital media quickly and effectively.
- Business Intelligence: Companies can also make use of grid computing to process and analyze large amounts of data in real-time. This can help businesses make informed decisions based on sound analysis. It also helps to monitor market trends, ensure risk management, and assess sales.
- Government and Defense: Governments can also use grid computing to process critical data for the safety and defense of the nation.
Examples of Grid Computing
Some of the real-life examples in action include:
- World Community Grid – WCG aka World Community Grid This is a distributed computing platform that allows users to donate their unused computing power to scientific research projects.
- The European Grid Initiative – Similarly, the European Grid Initiative is a large-scale grid computing project that provides access to computing resources for scientific research and industry.
- National Science Foundation’s TeraGrid project – Lastly, this TeraGrid Project provides access to some of the world’s largest and fastest supercomputers for scientific research.
Grid computing is a great concept to make use of your computing resources and keep your company running efficiently and optimally.





